HP ProLiant ML330e Drive technology overview
HP ProLiant ML330e Manual
 |
View all HP ProLiant ML330e manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
HP ProLiant ML330e manual content summary:
- HP ProLiant ML330e | Drive technology overview - Page 1
server disk drives ...2 Characteristics of disk drives ...3 Small form factor and large form factor disk drives 3 Disk drive capacity...4 Disk with RAID 9 Advanced controllers ...9 Solid state drives for servers...9 HP solid state drive reliability requirements 10 NAND over provisioning and - HP ProLiant ML330e | Drive technology overview - Page 2
. Typical intended applications for Entry drives are internal/archival storage or as boot disks for entry-level servers. HP Midline drives provide larger capacity and greater reliability than Entry drives. HP Midline drives have improved resistance to rotational and operational vibration, so they - HP ProLiant ML330e | Drive technology overview - Page 3
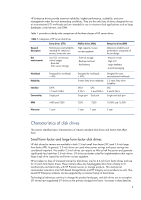
three classes of HP server drives. Table 1. Categories of HP server disk drives General description Use environments Entry drives (ETY) Performance and reliability intended for entry-level servers, lowest unit cost Low I/O, non-mission critical usages - Boot disk - Entry server storage Midline - HP ProLiant ML330e | Drive technology overview - Page 4
end of 2010, all new enterprise class drives and all new 10k and 15k RPM drives will be SFF. HP expects to continue to develop 3.5-inch midline and entry class drives. Disk drive capacity The capacity of a drive, measured in gigabytes, is set at manufacturing. Today's drives are capable of storing - HP ProLiant ML330e | Drive technology overview - Page 5
the bit density per unit length of track also helps increase the rate at which data can be written to and read from the drive. Disk I/O strategies are used to reduce the time that a logical read/write spends waiting for the physical read/write operation. These strategies seek to effectively decouple - HP ProLiant ML330e | Drive technology overview - Page 6
vibration problems. This can occur when using Entry or Midline drives with Enterprise class I/O workloads. In fact, Entry drives are not supported in the disk drives it ships remain reliable, meet customer requirements, and integrate seamlessly into HP server and storage systems. The HP processes - HP ProLiant ML330e | Drive technology overview - Page 7
HP option kitting configuration sites. Product quality data is reviewed on a daily, weekly, and monthly basis. Interconnect technology Various interconnect technologies are used to connect one or more disk -standard servers 2nd 6m 10 m Number of devices supported Command set 1 per link 2-6 - HP ProLiant ML330e | Drive technology overview - Page 8
were first introduced with HP ProLiant G6 servers in 2009. The SAS-2 interface will support SAS and SATA drives; however, the 6 Gb/s link speed is only achieved using new SAS-2 compliant disk drives. SAS-2 also supports SAS expanders to create a SAS fabric supporting large numbers of drives - HP ProLiant ML330e | Drive technology overview - Page 9
," at http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManual/c00687518/c00687518.pdf. Solid state drives for servers Solid state drives represent a new type of storage technology that is now mature enough to be used for server storage requirements. Unlike traditional disk drives, SSDs store data - HP ProLiant ML330e | Drive technology overview - Page 10
HP solid state drive reliability requirements As with traditional disk drives, all SSDs are not the same. HP engineering has applied a great deal of effort to ensure that HP server regions in the NAND flash array itself. All HP ProLiant SSDs feature power loss protection, which ensures that in - HP ProLiant ML330e | Drive technology overview - Page 11
is as good as or better than Enterprise class disk drives. SSDs are differentiated primarily by the read/write workload levels that they are able to support and their endurance, or expected service life. The current 2nd generation HP SSDs introduced in late 2009 are considered Enterprise mainstream - HP ProLiant ML330e | Drive technology overview - Page 12
should be viewed differently from that of disk drives. A server SSD that has reached the end of its service life is almost sure to start failing 20,000 + HP SAS SSD's (preliminary) Enterprise performance 6 Gb/s SAS-2 Dual Port TBD TBD 560 MB/s Up to 100,000 Conclusion Disk technology is evolving - HP ProLiant ML330e | Drive technology overview - Page 13
http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/Support Manual/c00301688/c00301688.pdf http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/Support Manual/c01613420/c01613420.pdf Technology brief Solid state drive technology for ProLiant servers http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManu al/c01580706

1
Abstract
..............................................................................................................................................
2
Introduction
.........................................................................................................................................
2
Categories of server disk drives
.............................................................................................................
2
Characteristics of disk drives
.................................................................................................................
3
Small form factor and large form factor disk drives
..............................................................................
3
Disk drive capacity
...........................................................................................................................
4
Disk drive performance
.....................................................................................................................
4
Reliability
........................................................................................................................................
5
Drive qualification process
....................................................................................................................
6
Interconnect technology
........................................................................................................................
7
Serial Attached SCSI (SAS)
...............................................................................................................
7
SAS-2
.............................................................................................................................................
8
Second generation Serial ATA (SATA)
................................................................................................
8
Interconnect bandwidths and drive throughput
.....................................................................................
8
Improved performance and reliability with RAID
......................................................................................
9
Advanced controllers
...........................................................................................................................
9
Solid state drives for servers
..................................................................................................................
9
HP solid state drive reliability requirements
........................................................................................
10
NAND over provisioning and wear-levelling
..................................................................................
10
Power loss protection
..................................................................................................................
10
Value, mainstream and performance SSDs
........................................................................................
11
SSD performance
...........................................................................................................................
12
Conclusion
........................................................................................................................................
12
For more information
..........................................................................................................................
13
Call to action
....................................................................................................................................
13
Drive technology overview
technology brief, 3
rd
edition