Asus P3C-D P3C-D User Manual - Page 22
System Memory
 |
View all Asus P3C-D manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 22 highlights
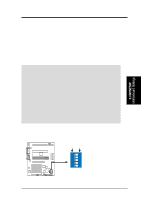
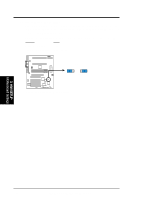
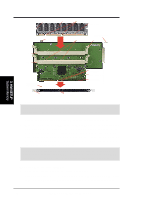
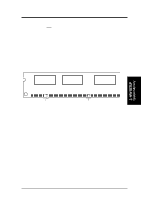
3. H/W SETUP System Memory 3. HARDWARE SETUP 3.5 System Memory NOTE: No hardware or BIOS setup is required after adding or removing memory. This motherboard has three Rambus Inline Memory Module (RIMM) sockets. The first two sockets (see Important notes for details) support Direct RDRAMs (both ECC and non-ECC are supported) in 64, 96, 128, 192, 256, and 512MB densities for a maximum of 1GB. With the optional ASUS DR1 DIMM Riser, unbuffered Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory (SDRAM, 3.3V power level) in 64, 128, 256, or 512MB densities with Serial Presence Detect (SPD) can be used on the third socket for a maximum of 1GB. The chipset's Error Checking and Correction (ECC) feature is available only when using RDRAMs. ECC feature is not available when using SDRAM with an ASUS DIMM Riser (ECC memory modules may still be used, but the ECC function will not be available). For memory speed setup, see 4.4.1 CHIP Configuration. IMPORTANT General 1. DO NOT attempt to mix RDRAMs with an SDRAM+Riser or vice versa. RDRAM 1. If more than one socket will be populated with RDRAMs, RIMM0 must be populated first and then RIMM1. The bundled ASUS CTRIMM must be used in RIMM2. If only one socket will be populated, RIMM0 must be populated with RDRAM, RIMM1 with the CTRIMM, and RIMM2 with the C-RIMM. See table for an overview. SDRAM 1. To use SDRAM with this motherboard, an ASUS DR1 DIMM Riser must be installed as an interface (see 3.5.2 Installing Memory Using the ASUS DR1 DIMM Riser). The riser must (and can only) be inserted into RIMM2, with the bundled C-RIMMs inserted into RIMM0 and RIMM1. See table for an overview. 2. When populating both DIMM sockets in the riser, the module density on J1M2 must be greater than the one on J1M1. 3. This motherboard's chipset only supports 64Mbit and 128Mbit SDRAMs (see SDRAM Configurations). 32Mx4 128 Mbit support is for registered DIMMs only. 4Mx16 64 Mbit support is for unbufferred DIMMs only. C-RIMM/CTRIMM 1. Depending on your configuration, a C-RIMM (Continuity RIMM) or CTRIMM, or both must be used to complete the sockets that are not populated by either RDRAMs or an ASUS DIMM Riser (when using SDRAM). C-RIMM is necessary to avoid breaking the signal lines, which are a serial connection in a Rambus interface, such as used in this motherboard. CTRIMM is used to minimize signal reflections or control the impedance at the end of the signal line. Both CRIMM and CTRIMM assure the electrical integrity of a Rambus interface. 22 ASUS P3C-D User's Manual