Canon EOS Rebel T3i 18-135mm IS Lens Kit Digital Photo Professional 3.10 for W - Page 68
Emphasize Distance, Emphasize Periphery, Emphasize Center, Advanced, Image Editing, and Printing
 |
View all Canon EOS Rebel T3i 18-135mm IS Lens Kit manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 68 highlights
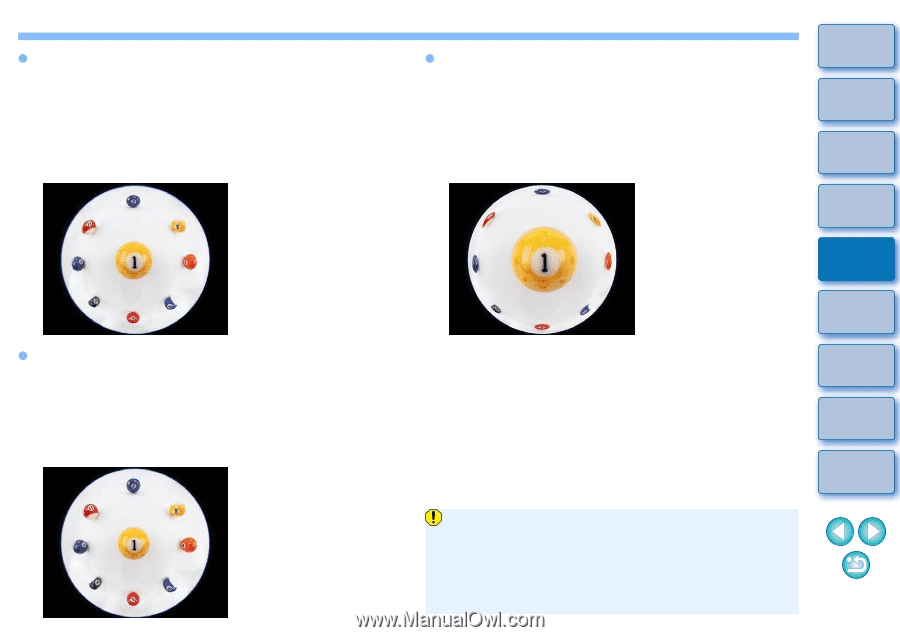
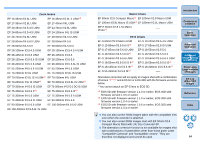
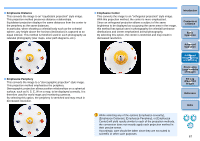
O Emphasize Distance This converts the image to an "equidistant projection" style image. This projection method preserves distance relationships. Equidistant projection displays the same distances from the center to the periphery as the same distances. In particular, when shooting a celestial body such as the celestial sphere, any height above the horizon (declination) is captured at an equal interval. This method is therefore used in such photography as celestial photography (star maps, solar path diagrams, etc.). O Emphasize Periphery This converts the image to a "stereographic projection" style image. This projection method emphasizes the periphery. Stereographic projection allows position relationships on a spherical surface, such as N, S, E, W on a map, to be displayed correctly. It is therefore used for world maps and monitoring cameras. By selecting this option, the periphery is stretched and may result in decreased resolution. O Emphasize Center This converts the image to an "orthogonal projection" style image. With this projection method, the center is more emphasized. Since an orthogonal projection allows a subject of the same brightness to be displayed as occupying the same area in the image, this method has typical uses in photography for celestial luminance distributions and center-emphasized animal photography. By selecting this option, the center is stretched and may result in decreased resolution. Introduction Contents at a Glance 1Basic Operation 2Advanced Operation 3Advanced Image Editing and Printing 4 Processing Large Numbers of Images 5Editing JPEG/TIFF Images Reference Index While selecting any of the options [Emphasize Linearity], [Emphasize Distance], [Emphasize Periphery], or [Emphasize Center] will yield results similar to each of the projection methods, the conversion does not exactly apply each projection method in their precise sense. Accordingly, care should be taken since they are not suited to scientific or other such purposes. 67