Casio FX 260 User Manual - Page 14
Trigonometric/Inverse Trigonometric, Functions
 |
UPC - 079767157289
View all Casio FX 260 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 14 highlights
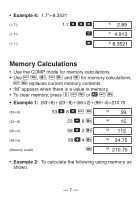
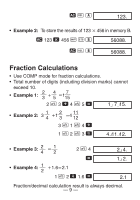
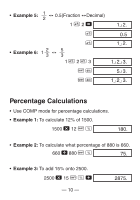
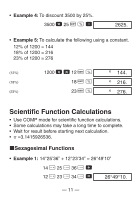
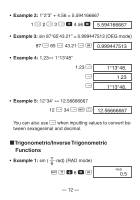
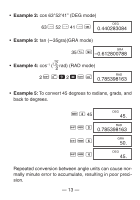
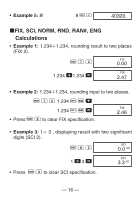
• Example 2: 1°2'3" + 4.56 = 5.594166667 1 I 2 I 3 I + 4.56 = 5.594166667 • Example 3: sin 87°65'43.21" = 0.999447513 (DEG mode) 87 I 65 I 43.21 I S 0.999447513 • Example 4: 1.23↔ 1°13'48" 1.23 I I I 1°13°48. 1.23 1°13°48. • Example 5: 12°34' ↔ 12.56666667 12 I 34 I A O 12.56666667 You can also use I when inputting values to convert between sexagesimal and decimal. kTrigonometric/Inverse Trigonometric Functions • Example 1: sin ( 6 rad) (RAD mode) A x \ 6 = S RAD 0.5 - 12 -
— 12 —
•
Example 2:
1°2’3” + 4.56 = 5.594166667
1
I
2
I
3
I
+
4.56
=
•
Example 3:
sin 87°65’43.21” = 0.999447513 (DEG mode)
87
I
65
I
43.21
I
S
•
Example 4:
1.23
↔
1°13’48”
1.23
I
I
I
•
Example 5:
12°34’
↔
12.56666667
12
I
34
I
A
O
You can also use
I
when inputting values to convert be-
tween sexagesimal and decimal.
k
Trigonometric/Inverse Trigonometric
Functions
•
Example 1:
sin (
rad) (RAD mode)
A
x
\
6
=
S
0.5
5.594166667
0.999447513
1°13°48.
1.23
1°13°48.
12.56666667
RAD
±
6