Compaq ProLiant 1000 Virtual Interface (VI) Architecture - The New Open Standa - Page 3
Concept Overview
 |
View all Compaq ProLiant 1000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 3 highlights
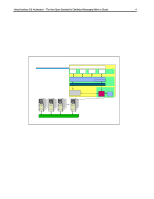
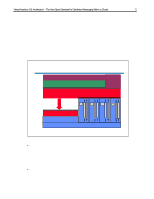
Virtual Interface (VI) Architecture - The New Open Standard for Distributed Messaging Within a Cluster 3 Concept Overview The Virtual Interface (VI) Architecture, authored and developed by Compaq, Intel, and Microsoft, is designed for hardware and software vendors and provides adapters, switches, middleware, and end-user application software that will seamlessly grow as servers or workstations are added and integrated into a clustered System Area Network (SAN). A SAN relies on high-speed, reliable messaging without the traditional communications protocol overhead as experienced by current LAN or WAN adapters and protocols, such as Ethernet, Token Ring, Fiber Channel Standard, Systems Network Architecture (SNA), or even Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM). The VI Architecture is to be used where server-to-server messages deal with application and data availability, and it allows any server error or failure to cause an immediate transfer of the business critical application to another server for uninterrupted processing. The architecture also allows for parallel application processing and minimizes performance bottlenecks where more traditional communications protocols such as the RPC, UDP, and Sockets have caused application processing delays due to protocol stack handling and/or network traffic overloads due to collision detection processing. These slowdowns cause application delays or inefficient use of the cluster. The VI Architecture specification has been reviewed by over 40 companies that have an interest in the specification and many have provided critiques and comments. These companies include hardware vendors such as Hitachi, HP, IBM, Pyramid Technologies, and Siemens-Nixdorf as well as software vendors such as Oracle, Informix, IBM Software Group, and SAP. ECG098/0998