Compaq ProLiant 1000 Drive technology overview - Page 11
Value, mainstream and performance SSDs
 |
View all Compaq ProLiant 1000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 11 highlights
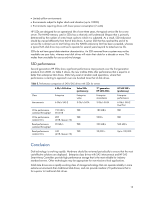
sustain a loss of power without requiring the lengthy metadata rebuild process required for SSDs that do not have this feature. Value, mainstream and performance SSDs As with spinning media, HP will introduce SSDs to meet the requirements of different application environments. All HP SSDs are considered Enterprise class devices since they deliver I/O performance, particularly read performance that is as good as or better than Enterprise class disk drives. SSDs are differentiated primarily by the read/write workload levels that they are able to support and their endurance, or expected service life. The current 2nd generation HP SSDs introduced in late 2009 are considered Enterprise mainstream storage devices. They are intended for use in workload constrained environments and are designed to have a 3 year service life. The first Enterprise performance SSDs are expected to be available sometime in 2010. These devices will be designed for use in unconstrained workload environments. Enterprise value SSDs will be designed to provide relatively large storage capacities at lower costs, but will not have the endurance of the mainstream or performance SSDs. Table 4 compares the endurance and reliability characteristics of the different types of SSDs that HP plans to offer. Table 4. Comparison of HP solid state drives and classes Value SATA SSDs (2010/2011) 2nd generation SATA SSDs (2009) Class Enterprise value Enterprise mainstream General description SFF and LFF Hot Plug SFF and LFF Hot Plug ML, DL, BL platforms Capacities 400 - 500 GB 60 GB and 120 GB 1st generation 6 GB SAS SSDs (2010) Enterprise performance SFF and LFF Hot Plug ML, DL, BL platforms 200 GB + NAND technology Workload Reliability Endurance Data Retention MLC Constrained write workloads < 30% writes,