Dell PowerConnect 2708 User's Guide - Addendum - Page 2
Configuring Interface Parameters, VLANs, they are attached. - managed mode
 |
View all Dell PowerConnect 2708 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 2 highlights
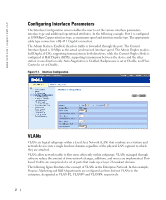
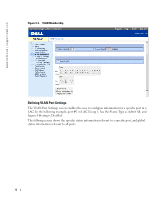
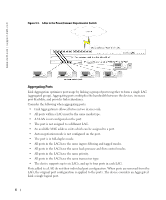
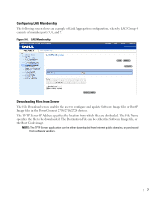
www.dell.com | support.dell.com Configuring Interface Parameters The Interface Configuration screen enables the user to set the various interface parameters, interface type and additional operational attributes. In the following example, Port 1 is configured as 1000Mbps Copper interface type, as maximum speed and interface media type. The appropriate cable type connection is RJ-45 1 Gigabit connection. The Admin Status is Enabled, therefore traffic is forwarded through the port. The Current Interface Speed is 10 Mbps as the actual synchronized interface speed. The Admin Duplex mode is Full Duplex (FDX), supporting transmission in both directions, while the Current Duplex Mode is configured at Half Duplex (HDX), supporting transmission between the device and the other station in one direction only. Auto-Negotiation is Enabled, Backpressure is set at Disable, and Flow Control is set at Disable. Figure 9-1. Interface Configuration VLANs VLANs are logical subgroups within a Local Area Network (LAN) that combine user stations and network devices into a single brodcast domain, regardless of the physical LAN segment to which they are attached. VLANs allow network traffic to flow more efficiently within subgroups. VLANs managed through software reduce the amount of time network changes, additions, and moves are implemented. Portbased VLANs are comprised of a set of ports that make up a Layer 2 broadcast domain. The following figure illustrates the concept of VLANs in the Enterprise Network. In this example, Finance, Marketing and R&D departments are configured as three distinct VLANs in the enterprise, designated as VLAN #2, VLAN#3 and VLAN#4, respectively. 2