Dell PowerEdge 2900 Information Update - Page 20
CPU Information Screen, Integrated Devices Screen - specifications
 |
View all Dell PowerEdge 2900 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 20 highlights
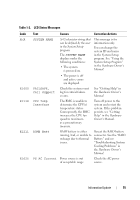
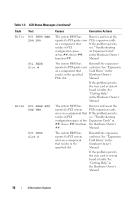
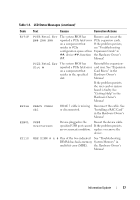
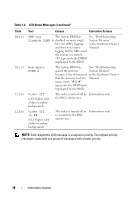
CPU Information Screen Table 1-4 updates the description for the Demand-Based Power Management option. Table 1-4. CPU Information Screen Option Demand-Based Power Management (Enabled default) Description NOTE: Check your operating system documentation to verify if the operating system supports this feature. Enables or disables demand-based power management. When enabled, the CPU Performance State tables are reported to the operating system; when disabled, the CPU Performance State tables are not reported to the operating system. If any of the CPUs do not support demand-based power management, the field becomes read-only, and is automatically set to Disabled. Integrated Devices Screen Table 1-5 lists new Integrated Devices screen options. Table 1-5. Integrated Devices Screen Options Option Description Internal USB Port Enables or disables the system's internal USB port. (On default) OS Watchdog Timer (Disabled default) NOTE: This feature is usable only with operating systems that support WDAT implementations of the Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) 3.0b specification. Microsoft® Windows Server® 2008 supports this feature, but Windows Server 2003 does not. Sets a timer that monitors the operating system for activity and aids in recovery if the system stops responding. When this field is set to Enabled, the operating system is allowed to initialize the timer. When set to Disabled, the timer is not initialized. I/OAT DMA Engine (Disabled default) Enables or disables the I/O Acceleration Technology (I/OAT) option. When set to Enabled, I/OAT reduces system CPU usage for applications that use TCP by offloading part of TCP receive operation to the DMA engine. 20 Information Update