HP 127695-B21 Smart Array Controller Technology: Drive Array Expansion and Ext - Page 8
stripe size migration, conclusion, Larger stripes for RAID 0, RAID 0+1
 |
UPC - 743172872142
View all HP 127695-B21 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 8 highlights
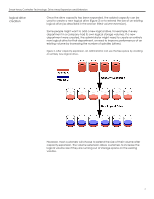
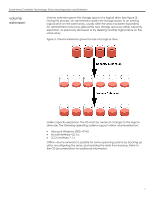
Smart Array Controller Technology: Drive Array Expansion and Extension stripe size migration When an administrator expands the volume capacity of an array, this does nothing to change the stripe size of the data stored within the array. Each RAID level has a default value designed to provide good performance across many types of applications (see table 2). In addition, table 2 shows the range of stripe sizes available per RAID level. If an administrator changes the RAID level, and this new RAID level does not support the existing stripe size, the ACU or ACU-XE changes the stripe size automatically. table 2. Stripe sizes available per RAID level Fault Tolerance Level Default (KB) RAID 0 128 RAID 1 or 0+1 128 RAID 5 16 RAID ADG 16 Available Stripe Sizes (KB) 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256 8, 16, 32, 64 8, 16, 32, 64 Certain applications, especially those that perform a majority of one type of transaction (for example, primarily write transactions), may require tuning of the stripe size to increase performance. Table 3 recommends stripe sizes for general types of server applications. An administrator can take these general recommendations and try progressively larger or smaller stripe sizes to determine the best overall performance for a particular application. Through ACU or ACU-XE, the administrator can make these changes online without disruption or data loss. table 3. Recommended stripe sizes Type of Server Application Mixed read/write Mainly sequential read (such as audio/video applications) Mainly write (such as image manipulation applications) Suggested Stripe Size Change Accept default value Larger stripe sizes Smaller stripes for RAID 5, RAID ADG Larger stripes for RAID 0, RAID 0+1, RAID 1 conclusion Capacity expansion simply adds drives to an array. This may improve performance by increasing the number of spindles available. However, most customers will want to take advantage of this newly available space by either creating a new logical drive or extending the size of an existing one. An administrator can also change RAID levels or stripe sizes as needed for performance or fault-tolerance improvements. The management software included with the Smart Array Controllers makes all these functions available online to eliminate the need for administrators to shut down the server to reconfigure their storage. 8