HP 2000fc RAID 6 with HP Advanced Data Guarding technology: a cost-effective, - Page 9
Choosing a RAID level, Summary
 |
View all HP 2000fc manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 9 highlights
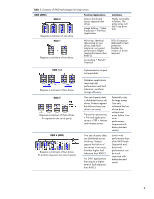
Choosing a RAID level To choose the optimum RAID level for data protection in large arrays, IT managers should consider a variety of factors, including: • Fault tolerance (based on availability requirements) • Cost effectiveness (based on storage efficiency or cost per gigabyte of usable capacity) • Performance The decision chart in Table 3 is an aid for determining which RAID level will provide the best solution for a specific computing environment. For example, if cost effectiveness is of primary importance and fault tolerance is of secondary importance, or vice versa, the best choice is RAID 6. Table 3: Decision chart for choosing the optimum RAID level for large arrays Most important Cost effectiveness Fault tolerance Performance Secondary importance Fault tolerance → Performance → Cost effectiveness→ Performance → Cost Effectiveness→ Fault tolerance → RAID level choice RAID 6 (ADG) RAID 5 (RAID 0 if fault tolerance is not needed) RAID 6 (ADG) RAID 1+0 RAID 5 (RAID 0 if fault tolerance is not needed) RAID 1+0 Summary RAID 6 with HP's patented Advanced Data Guarding technology provides an advanced level of data protection for computing environments requiring a higher level of fault tolerance than RAID 5 and a lower implementation cost than RAID 1. RAID 6 is best implemented when IT organizations need to protect enterprise data at a lower cost than RAID 1 arrays and when performance is not an overriding factor. RAID 6 can effectively protect an array of up to the maximum number of drives supported by a variety of Smart Array Controllers. A RAID 6 array can tolerate up to two simultaneous drive failures without downtime or data loss. RAID 6 supports Online Spare Drives and Online RAID Level Migration from any RAID level. 9