HP DL360 Power basics for IT professionals - Page 22
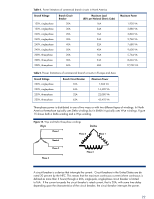
Delta, Table 4., Branch Voltage, Branch Circuit, Breaker, Maximum Load, per National Electric Code
 |
UPC - 613326948835
View all HP DL360 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 22 highlights
Table 4. Power limitations of commercial branch circuits in North America Branch Voltage 120V, single-phase 120V, single-phase 240V, single-phase 240V, single-phase 240V, single-phase 240V, single-phase 208V, three-phase 208V, three-phase 208V, three-phase Branch Circuit Breaker 20A 30A 20A 30A 40A 50A 20A 30A 60A Maximum Load (80% per National Electric Code) 16A 24A 16A 24A 32A 40A 16A 24A 48A Maximum Power 1,920 VA 2,880 VA 3,840 VA 5,760 VA 7,680 VA 9,600 VA 5,764 VA 8,646 VA 17,292 VA Table 5. Power limitations of commercial branch circuits in Europe and Asia Branch Voltage 230V, single-phase 230V, single-phase 230V, three-phase 230V, three-phase Branch Circuit Breaker 32A 63A 32A 63A Maximum Power 7,360 VA 14,490 VA 22,080 VA 43,470 VA Three-phase power is distributed in one of two ways or with two different types of windings. In North America three-phase typically uses Delta windings but in EMEA it typically uses Wye windings. Figure 15 shows both a Delta winding and a Wye winding. Figure 15. Wye and Delta three-phase windings Wye Delta Phase 1 Phase 3 Phase 1 Neutral Phase 2 Phase 3 Phase 2 A circuit breaker is a device that interrupts the current. Circuit breakers in the United States are derated 20 percent by the NEC. This means that the maximum continuous current (where continuous is defined as more than 3 hours) through a 20A, single-pole, single-phase circuit breaker is limited to16A. If the current exceeds the circuit breaker's rated current, that is 20A, with some time delay depending upon the characteristics of the circuit breaker, the circuit breaker interrupts the power. 22