HP Dc7100 Operating System and Device Driver Support for 2004 HP Compaq Busine - Page 3
Acronyms used
 |
UPC - 829160356877
View all HP Dc7100 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 3 highlights
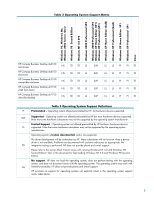
Acronyms used • 48-Bit LBA - Logical block Addressing. 28-bit LBA allows the use of hard drives up to 137 GB. 48-bit LBA allows the use of hard drives significantly over 137 GB. For more information see http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;en-us;303013 or http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;305098 • APM/APCI - APM (Advanced Power Management) is a legacy power management scheme that was first widely supported in Microsoft® Windows® 95. Most of the interesting functionality for APM is in a machine-specific BIOS that is hidden from the operating system. APM is a legacy solution that has been superseded by ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface), which is the robust scheme for power management and system configuration supported in the Windows 98 and Windows 2000 family of operating systems. Windows XP uses ACPI. For more information see: http://www.microsoft.com/whdc/archive/apm.mspx http://www.microsoft.com/whdc/archive/w2apm.mspx • APIC - an advanced programmable interrupt controller (APIC) scheme used by all PCs currently in production. It consists of a local APIC which delivers interrupts to a specific processor and an I/O APIC which collects interrupt signals from I/O devices and sends messages to the local APICs when those devices need to interrupt. Each I/O APIC has an arbitrary number (typically 24) of interrupt inputs. For more information see: http://www.microsoft.com/whdc/system/sysperf/IO-APIC.mspx http://www.microsoft.com/whdc/system/sysperf/apic.mspx • BIOS - Basic Input/Output System: The system's firmware which allows the power up of various devices during boot for the OS to load properly. • HP - means that these device drivers are available from the HP Web site: http://h18007.www1.hp.com/support/files/index.html • HP/WU - means that drivers are available from both the HP Web site (Softpaq) and from Windows Update. HP has tested and validated that the device drivers on the HP Web site function as expected with the operating systems that are listed as supported in Table 3 Operating System Support Definitions. • HPQFlash - HPQFlash is a BIOS update utility used from within Windows from Hewlett-Packard that updates the read-only-memory (ROM) chip on the system board. • N/R - means "not recommended." • OS - means that support is included with the operating system. • PIC - A programmable interrupt controller (PIC) scheme first used in the IBM PC/AT from the 1980s that used two Intel 8259 programmable interrupt controllers. Each 8259 had eight interrupt inputs (IRQs). The second interrupt controller was connected to the first interrupt controller leaving fifteen interrupt inputs available for all devices in a PC. • ROMPAQ - ROMPAQ is a BIOS update utility on a bootable diskette from Compaq (now Hewlett-Packard) that updates the read-only-memory (ROM) chip on the system board. • SP - Service Pack • 98SE - refers to Microsoft Windows 98 Second Edition • Me - refers to Microsoft Windows Millennium Edition • NT4 - refers to Microsoft Windows NT 4.0 • 2000 - refers to Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional • W2K-SP3 - refers to Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional Service Pack 3 • W2K-SP4 - refers to Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional Service Pack 4 • WXP-SP1a - refers to Microsoft Windows XP Service Pack 1a • WXP-SP2 - refers to Microsoft Windows XP Service Pack 2 3