HP Nc6220 Bluetooth Wireless Technology Basics - Page 5
BWT security, - specifications
 |
View all HP Nc6220 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 5 highlights
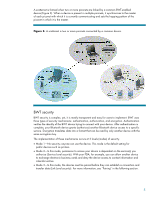
A scatternet is formed when two or more piconets are linked by a common BWT-enabled device (Figure 3). When a device is present in multiple piconets, it synchronizes to the master of each piconet with which it is currently communicating and sets the hopping pattern of the piconet in which it is the master. Figure 3. A scatternet is two or more piconets connected by a common device. BWT security BWT security is complex; yet, it is mostly transparent and easy for users to implement. BWT uses three types of security mechanisms: authentication, authorization, and encryption. Authentication verifies the identity of the BWT device trying to connect with your device. After authentication is complete, your Bluetooth device grants (authorizes) another Bluetooth device access to a specific service. Encryption translates data into a format that can be read by only another device with the same encryption key. The implementation of these mechanisms occurs at 3 levels (modes) of security: • Mode 1-No security; anyone can use the device. This mode is the default setting for public devices such as printers. • Mode 2-In this mode, permission to access your device is dependent on the service(s) you authorize (Service Level security). With your PDA, for example, you can allow another device to exchange electronic business cards and deny the device access to contact information and calendar entries. • Mode 3-In this mode, the devices must be paired before they can establish a connection and transfer data (Link Level security). For more information, see "Pairing" in the following section. 5