HP Pavilion 9800 HP Pavilion PC's - (English) 1394U User's Manual - Page 2
What is IEEE 1394, Features - power supply
 |
View all HP Pavilion 9800 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 2 highlights
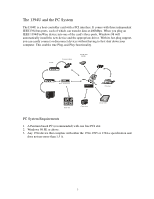
What is IEEE 1394 The 1394 standard was defined, and continues to be maintained, by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc. (IEEE). The technology allows for high-speed connections between computers and related devices and helps bridge the divide between computers and consumer electronics. The technology is flexible, easy to use and offers high bandwidth at a low cost. With 1394-compatible products and systems, users can transfer video or still images from a camera or camcorder to a printer, PC, or television quickly, with no image degradation. 1394 Features The 1394 standard is a high-speed serial bus designed to deliver high data transfer speeds at a low cost, and with the low degree of latency required by a peripheral bus or by a backup to a traditional parallel bus. Among its key features are: N High Speed. Speeds of 100, 200 and 400 megabits per second (Mbps) are currently supported. N Isochronous Support. Deterministic bandwidth allocation guarantees bandwidth for time-sensitive applications, such as real-time video feeds, that could otherwise be disrupted by heavy bus traffic. N Flexible Topology. Devices can be daisy-chained and no central bus supervision is required. N Hot-Plug Support. The bus is dynamically reconfigured whenever new nodes are added, which means users don't have to configure node IDs or unique termination schemes. N Cable Power. Low-cost peripherals can be powered directly from the 1394 cable, so no dedicated power supply is needed. N Open IEEE Standard. IEEE adoption has increased industry acceptance of the standard. N Optimum Performance. Each cable connection can be up to 4.5 meters long, yielding a total cable distance of 72 meters. N 1394 End devices. IEEE 1394 interfaces have already been incorporated into a variety of devices, including PC cameras, DV camcorders, DV recorders, digital still cameras, high-speed hard disk drives, CD-ROM drives, DVD-ROM drives, DVDRAM drives, digital TVs, set-top boxes, scanners, and printers. 2