HP ProLiant DL288 Visualization and Acceleration in HP ProLiant servers - Page 3
Acceleration
 |
View all HP ProLiant DL288 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 3 highlights
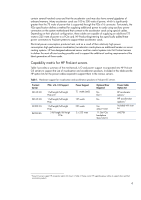
Visualization application areas The rapid advances in GPU technology have made possible a level of performance for Visualization applications on industry-standard platforms that was unimaginable a decade ago. Currently visualization applications are used in several industries: Computer Aided Design and Computer Aided Engineering - Fluid Dynamics - Finite element analysis Oil and gas exploration - Mapping seismic data - Reservoir modeling Medical and life sciences - Medical image rendering - Molecular models Visualization applications on servers Although Visualization applications are frequently run on workstations, they can also be run on a server. This is often referred to as a remote Visualization configuration, since the graphic output from the Visualization application is typically piped to a desktop for viewing using remote viewing software such as HP Remote Graphics Software or other 3rd party products. There are several advantages to running Visualization applications on servers. Server processor and memory resources. Servers can provide more processors and larger memory configurations than many workstations. These may be needed when running more challenging applications. Resource sharing. Using a high-end server in a remote visualization configuration allows it to be shared by members of an organization needing to run Visualization applications Centralization of data. The large data sets involved in Visualization applications can be stored, accessed and managed more easily. Remote viewing software moves just the images to the desktop. This saves time, file space and back-up resources, and also provides increased security. Remote management. Servers have advanced monitoring and remote management features. This allows them to be b Acceleration Acceleration is a general term for hardware technologies that are designed to significantly speed up computationally intense tasks and applications. Typically, these applications are scientific or engineering oriented, although advanced business applications can also be computationally intense. The numeric co-processors from the first few years of industry- standard computing are an early example of acceleration technology. Acceleration usually involves processing very large data sets using very complex or iterative numerical calculations, typically involving floating point math. These tasks can be accomplished on industry standard servers using general purpose multi-core CPUs. In recent years, however, vendors have created cost-effective Acceleration products that provide up to an order of magnitude better performance for these applications running on industry standard computers. 3