HP ProLiant DL380p ISS Technology Focus, Number 14 - Page 2
Full Data-Path Error Detection, Surprise power loss protection, SmartSSD Wear Gauge
 |
View all HP ProLiant DL380p manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 2 highlights
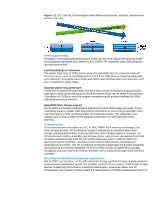
Figure 1-1: SLC and MLC technologies have different endurance, retention, performance, density, and cost. HP Enterprise SSDs In addition to providing high performance, SSDs are far more robust that spinning media drives against high shock and vibration up to 1000G. HP enterprise class SSDs features are described below. Full Data-Path Error Detection The higher data rates of SSDs can increase the probability that an unreported data bit error can occur, such as a bit flipping from 1 to 0 if the SSD does not have full data-path error detection. Enterprise class SSDs and HDDs have full data-path error detection, and error correction in some cases. Surprise power loss protection Power loss protection ensures that if the drive loses power (including hot plug removal), user data in write cache still writes to the drive and the drive can be ready in a short time. This allows HP SSDs to avoid the lengthy metadata rebuild process required for SSDs without power-loss protection. SmartSSD Wear Gauge support All HP SSDs incorporate sophisticated features to monitor SSD usage and wear. These monitoring features enable tools that present information to you on the percentage of life used and amount of life remaining under the workload-to-date. This information can validate your choice of SSD for the application and help you with SSD end-of-life planning. IO accelerators I/O accelerators are also based on SLC or MLC NAND flash memory technology. Like other storage devices, I/O accelerators present themselves as standard block level storage, allowing applications to access them like other storage volumes. However, an I/O Accelerator is both a controller and storage device, with its own specialized driver that translates standard block level I/O into NAND reads and writes. It delivers block I/O directly across the PCIe bus, resulting in lower latency performance advantages in particular environments. The I/O accelerator architecture leverages the greater bandwidth and multi-core processing capabilities of server CPUs to achieve higher block storage throughput and lower latencies than are possible with a traditional storage stack and drive controller. HP enterprise SSD and IO accelerator applications Not all SSDs are the same, so the HP solid-state storage portfolio includes multiple products to meet various application needs. Our portfolio consists of four classes of solid-state storage devices: Enterprise Performance, Enterprise Mainstream, Enterprise Value, and IO Accelerators. Each class of device meets the requirements of different applications shown in