HP ProLiant ML310e DDR3 memory technology - Page 11
Memory throughput with DDR3
 |
View all HP ProLiant ML310e manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 11 highlights
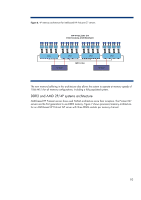
Figure 7. 4P memory architecture for AMD-based HP ProLiant G7 servers DDR3 DIMMs CPU HP ProLiant G7 AMD 4-way architecture DDR3 DIMMs DDR3 DIMMs DDR3 DIMMs CPU CPU CPU HyperTransport Links The AMD-based ProLiant G7 servers use essentially the same processor/memory architecture for both 2P and 4P systems. Each processor has 4 memory controllers, each with a channel supporting either two or three DDR3 DIMMs, depending on the system. The three DIMM memory channels are designed as a "T" electrically, with one DIMM installed at the center of the "T" and the other two DIMMs on the ends. This design provides improved signal integrity by keeping the lengths of the electrical paths to the DIMMs as close to the same length as reasonably possible. In order to help maintain this symmetry, DIMMs are installed on both ends of the "T" before the 3rd DIMM is installed in the center. This architecture allows the memory subsystem to support DDR3 operating at 1333 MT/s when memory channels are not fully populated. The absence of external memory buffering also results in lower overall memory latency. However, without buffering, the architecture can only support a maximum of 48 DIMMs, or 768 GB of system memory. Memory throughput with DDR3 System memory bandwidth By removing the front side bus and moving the memory controllers onto the processors, the newer system architectures eliminate some of the previous memory bottlenecks. The maximum theoretical memory bandwidth is unattainable in practice, since it represents an idealized scenario in which all memory channels are operating at full throughput all of the time. Using NUMA architectures, 2P ProLiant servers are now able to achieve significantly improved measured memory throughput relative to their theoretical maximums (Table 3). 11