HP ProLiant SL270s HP ProLiant SL6000 Scalable System technology - Page 14
Memory technologies, DDR3 memory enhancements, Controlled fan speed, Reduced operating voltage
 |
View all HP ProLiant SL270s manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 14 highlights
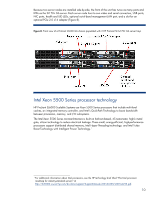
Figure 12. Diagram showing how the processor installation tool simplifies installation Memory technologies Xeon 5500 Series processors connect directly to memory rather than through a chipset. These processors support only DDR3 dual inline memory modules (DIMMs). DDR3 is part of the synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM) group of technologies. Administrators control all processor functionality options, including memory mirroring and memory channel interleaving, through the G6 server RBSU. DDR3 memory enhancements DDR3 has several key enhancements over DDR2 memory, including an 8-bit prefetch buffer for storing data before it is requested. DDR2 has a 4-bit buffer. For DDR3, the data signal rate can increase to 1333 megatransfers per second (MT/s). Although this is commonly referred to as having a speed of 1333 MHz, the maximum clock speed for the DIMMs is actually 667 MHz. The signal is doublepumped to achieve the data rate of 1333 MT/s. DDR3-1333 DIMMs can operate at clock speeds of 667 MHz, 533 MHz, and 400 MHz with corresponding data rates of 1333, 1066, and 800 MT/s. Controlled fan speed HP DDR3 DIMM modules have an integrated thermal sensor that signals the chipset to limit memory traffic to the DIMM if the DIMM temperature exceeds a programmable critical trip point. Using the data from these thermal sensors, ProLiant G6 servers can reduce fan speed when memory is idle, which reduces power consumption. The BIOS in ProLiant G6 servers verifies the presence of the thermal DIMM sensor during POST. Some third-party DIMMs may not include this DIMM thermal sensor. If the thermal sensor is absent, a POST message will warn that the DIMM does not have a thermal sensor, and the fans will run at higher speeds (requiring more power). Reduced operating voltage Operating voltage for DDR3 has been reduced: DDR2 operates at 1.8V, while at this writing DDR3 operates at 1.5V and consumes less power than DDR2 DIMMs at the same capacity and speed. Even though DDR3 DIMMs and DDR2 DIMMs are the same size and have the same number of pins, they have different key notch locations and are electrically incompatible. 14