HP Z820 Site preparation guide - HP Z800 Workstation 1110W power supply, HP Z8 - Page 7
Input current calculation - power supply
 |
View all HP Z820 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 7 highlights
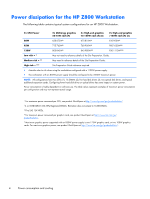
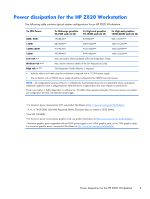
● Why use a UPS? Use a UPS for a fully loaded workstation configuration that operates in a poor power grid area. The UPS must be rated for at least 2 kVA. A UPS is necessary because without line conditioning to guarantee greater than 90 volts for 1110 or 1125 watts output and 105 volts for 1250 or 1275 watts output, the maximum output power is limited to 890 watts and 1110 or 1125 watts, respectively. See Power dissipation for the HP Z800 Workstation on page 4 for configurations and maximum power estimates. HP recommends an online continuous UPS that provides a layer of insulation from quality problems. This type of supply also allows control of output voltage and frequency regardless of input voltage and frequency. To reach 1250 or 1275 watts of output power, you must maintain 115 volts, ideally. ● To reduce the risk of overload: ◦ Do not exceed the rated load of any single power distribution unit (PDU). ◦ Do not load a single National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) 5 to 15 receptacle with more than 15 amps. ◦ Do not load a single International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 320-1/C13 receptacle with more than 10 amps. ◦ In general, verify that each power source circuit can safely provide the current required by equipment drawing power from it. Input current calculation The 1110W power supply can provide 1110 watts in a 15A circuit by using this input current calculation: Input Current = Output Power / (Voltage x Power Factor x Efficiency) Workstation HP Z800 HP Z820 Output Power = 1110 watts 1125 watts Voltage = 90 volts 90 volts Power Factor = 0.998 0.998 Efficiency = 0.82 0.835 In this formula, the voltage (90 volts) includes all power line variations-line voltage sag, brownout conditions, power grid characteristics, and so on. CAUTION: Check with your power provider to see if your facility is exposed to 90V power. If 90 volts cannot be guaranteed to your workstation, the input voltage source might blow the fuse in the power supply or trip the breaker. For reliable workstation operation under heavy loading, use a UPS because it provides reliable voltage levels. Input current calculation 3