JVC G15U Specifications - Page 3
age Quality - lamp
 |
View all JVC G15U manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 3 highlights
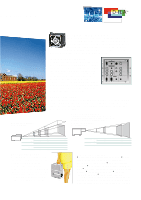
age Quality D-ILA™ - Projector Device Innovation D-ILA™ Structure The D-ILA™ device is a reflective type of LCD that delivers a higher aperture ratio (more than 93%) than a transmissive LCD panel, and is comprised of groups of pixels which correspond to each image dot. Also unlike conventional transmissive LCD panels (in which the driving transistor is mounted on the same surface as the pixels), the D-ILA™ʟs driving IC substrate is located behind the liquid crystal layer. As a result, the D-ILA™ device can achieve higher brightness and higher resolution at the same time. In addition, thanks to the vertical alignment ("homeotropic" structure) of the liquid crystal layer, projected images also have much higher contrast. Device Structure Front view Side view Driving IC (CMOS substrate) Planarized layer Reflective pixel electrode Input signal written directly in a form of electric signal Pixel Liquid crystal layer Transparent electrode Glass substrate D-ILA™ Operation The light from the xenon lamp travels through a polarized beam splitter (PBS), which is reflected off the D-ILA™ device, then passed through the projection lens and onto the screen. D-ILA™ device Operation Principle PBS (Polarized Beam Splitter) Input signal Lamp Projection lens Screen