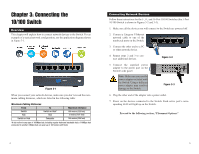
Linksys SD208 Cisco SD205, SD208, SD216 10/100 Switches Quick Start Guide - Page 7
Appendix B: Specifications - router
 |
UPC - 745883556823
View all Linksys SD208 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 7 highlights
Hub - The device that serves as the central location for attaching wires from workstations. Can be passive, where there is no amplification of the signals; or active, where the hubs are used like repeaters to provide an extension of the cable that connects to a workstation. Mbps (Megabits per second) - One million bits per second; unit of measurement for data transmission. MDI (Medium Dependent Interface) - On a network hub or switch, a MDI port, also known as an uplink port, connects to another hub or switch using a straight-through cable. To connect a MDI port to a computer, use a crossover cable. MDI-X (Medium Dependent Interface Crossed) - On a network hub or switch, a MDI-X port connects to a computer using a straight-through cable. To connect a MDI-X port to another hub or switch, use a crossover cable. Network - A system that transmits any combination of voice, video and/or data between users. Switch - 1. A data switch connects computing devices to host computers, allowing a large number of devices to share a limited number of ports. 2. A device for making, breaking, or changing the connections in an electrical circuit. Topology - A network's topology is a logical characterization of how the devices on the network are connected and the distances between them. The most common network devices include hubs, switches, routers, and gateways. Most large networks contain several levels of interconnection, the most important of which include edge connections, backbone connections, and wide-area connections. UTP - Unshielded twisted pair is the most common kind of copper telephone wiring. Twisted pair is the ordinary copper wire that connects home and many business computers to the telephone company. To reduce crosstalk or electromagnetic induction between pairs of wires, two insulated copper wires are twisted around each other. Each signal on twisted pair requires both wires. Since some telephone sets or desktop locations require multiple connections, twisted pair is sometimes installed in two or more pairs, all within a single cable. 8 Appendix B: Specifications Model Number Standards Ports SD205 SD208 SD216 Cabling Type LEDs SD205 SD208 SD216 SD205 5-Port 10/100 Switch SD208 8-Port 10/100 Switch SD216 16-Port 10/100 Switch IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.3u 5 RJ-45 10/100 8 RJ-45 10/100 16 RJ-45 10/100 Category 5 Ethernet System, Port Status 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 System, Port Status 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8 System, Port Status 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, and 16 9