Netgear DG834Gv1 DG834Gv2 Reference Manual - Page 177
Related Documents, Domain Name Server, IP Configuration by DHCP, Address
 |
View all Netgear DG834Gv1 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 177 highlights
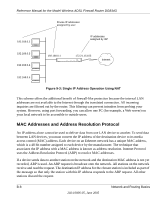
Reference Manual for the Model Wireless ADSL Firewall Router DG834G Related Documents The station with the correct IP address responds with its own MAC address directly to the sending device. The receiving station provides the transmitting station with the required destination MAC address. The IP address data and MAC address data for each station are held in an ARP table. The next time data is sent, the address can be obtained from the address information in the table. For more information about address assignment, refer to the IETF documents RFC 1597, Address Allocation for Private Internets, and RFC 1466, Guidelines for Management of IP Address Space. For more information about IP address translation, refer to RFC 1631, The IP Network Address Translator (NAT). Domain Name Server Many of the resources on the Internet can be addressed by simple descriptive names such as www.NETGEAR.com. This addressing is very helpful at the application level, but the descriptive name must be translated to an IP address in order for a user to actually contact the resource. Just as a telephone directory maps names to phone numbers, or as an ARP table maps IP addresses to MAC addresses, a domain name system (DNS) server maps descriptive names of network resources to IP addresses. When a PC accesses a resource by its descriptive name, it first contacts a DNS server to obtain the IP address of the resource. The PC sends the desired message using the IP address. Many large organizations, such as ISPs, maintain their own DNS servers and allow their customers to use the servers to look up addresses. IP Configuration by DHCP When an IP-based local area network is installed, each PC must be configured with an IP address. If the PCs need to access the Internet, they should also be configured with a gateway address and one or more DNS server addresses. As an alternative to manual configuration, there is a method by which each PC on the network can automatically obtain this configuration information. A device on the network may act as a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server. The DHCP server stores a list or pool of IP addresses, along with other information (such as gateway and DNS addresses) that it may assign to the other devices on the network. The DG834G wireless router has the capacity to act as a DHCP server. Network and Routing Basics B-9 202-10006-05, June 2005