Netgear WGM511 WGM511 Reference Manual - Page 64
Is WPA Perfect?, Temporal Key Integrity Protocol TKIP., Michael., AES Support.
 |
View all Netgear WGM511 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 64 highlights
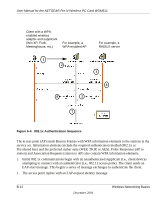
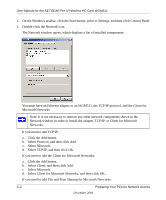
User Manual for the NETGEAR Pre-N Wireless PC Card WGM511 Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP). WPA uses TKIP to provide important data encryption enhancements including a per-packet key mixing function, a message integrity check (MIC) named Michael, an extended initialization vector (IV) with sequencing rules, and a re-keying mechanism. TKIP also provides for the following: • The verification of the security configuration after the encryption keys are determined. • The synchronized changing of the unicast encryption key for each frame. • The determination of a unique starting unicast encryption key for each preshared key authentication. Michael. With 802.11 and WEP, data integrity is provided by a 32-bit integrity check value (ICV) that is appended to the 802.11 payload and encrypted with WEP. Although the ICV is encrypted, you can use cryptanalysis to change bits in the encrypted payload and update the encrypted ICV without being detected by the receiver. With WPA, a method known as Michael specifies a new algorithm that calculates an 8-byte message integrity code (MIC) using the calculation facilities available on existing wireless devices. The MIC is placed between the data portion of the IEEE 802.11 frame and the 4-byte ICV. The MIC field is encrypted together with the frame data and the ICV. Michael also provides replay protection. A new frame counter in the IEEE 802.11 frame is used to prevent replay attacks. AES Support. One of the encryption methods supported by WPA beside TKIP is the advanced encryption standard (AES), although AES support will not be required initially for Wi-Fi certification. This is viewed as the optimal choice for security conscience organizations, but the problem with AES is that it requires a fundamental redesign of the NIC's hardware in both the station and the access point. TKIP was a pragmatic compromise that allows organizations to deploy better security while AES capable equipment is being designed, manufactured, and incrementally deployed. Is WPA Perfect? WPA is not without its vulnerabilities. Specifically, it is susceptible to denial of service (DoS) attacks. If the access point receives two data packets that fail the Message Integrity Code (MIC) check within 60 seconds of each other then the network is under an active attack, and as a result, the access point employs counter measures, which includes disassociating each station using the access point. This prevents an attacker from gleaning information about the encryption key and alerts administrators, but it also causes users to lose network connectivity for 60 seconds. More than anything else, this may just prove that no single security tactic is completely invulnerable. WPA is a definite step forward in WLAN security over WEP and has to be thought of as a single part of an end-to-end network security strategy. B-14 December 2004 Wireless Networking Basics