TP-Link TL-SL5428E User Guide - Page 76
Vlan Vpn
 |
UPC - 845973020873
View all TP-Link TL-SL5428E manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 76 highlights
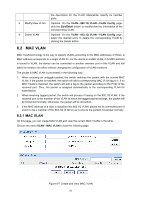
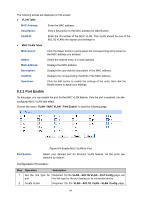
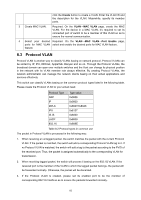
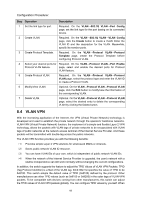
Configuration Procedure: Step Operation Description 1 Set the link type for port. Required. On the VLAN→802.1Q VLAN→Port Config page, set the link type for the port basing on its connected device. 2 Create VLAN. Required. On the VLAN→802.1Q VLAN→VLAN Config page, click the Create button to create a VLAN. Enter the VLAN ID and the description for the VLAN. Meanwhile, specify its member ports. 3 Create Protocol Template. Required. On the VLAN→Protocol VLAN→Protocol Template page, create the Protocol Template before configuring Protocol VLAN. 4 Select your desired ports for Required. On the VLAN→Protocol VLAN→Port Enable Protocol VLAN feature. page, select and enable the desired ports for Protocol VLAN feature. 5 Create Protocol VLAN. Required. On the VLAN→Protocol VLAN→Protocol VLAN page, select the protocol type and enter the VLAN ID to create a Protocol VLAN. 6 Modify/View VLAN. Optional. On the VLAN→Protocol VLAN→Protocol VLAN page, click the Edit button to modify/view the information of the corresponding VLAN. 7 Delete VLAN. Optional. On the VLAN→Protocol VLAN→Protocol VLAN page, select the desired entry to delete the corresponding VLAN by clicking the Delete button. 8.4 VLAN VPN With the increasing application of the Internet, the VPN (Virtual Private Network) technology is developed and used to establish the private network through the operators' backbone networks. VLAN-VPN (Virtual Private Network) function, the implement of a simple and flexible Layer 2 VPN technology, allows the packets with VLAN tags of private networks to be encapsulated with VLAN tags of public networks at the network access terminal of the Internet Service Provider. And these packets will be transmitted with double-tag across the public networks. The VLAN-VPN function provides you with the following benefits: (1) Provides simple Layer 2 VPN solutions for small-sized MANs or intranets. (2) Saves public network VLAN ID resource. (3) You can have VLAN IDs of your own, which is independent of public network VLAN IDs. (4) When the network of the Internet Service Provider is upgraded, the user's network with a relative independence can still work normally without changing the current configurations. In addition, the switch supports the feature to adjust the TPID Values of VLAN VPN Packets. TPID (Tag Protocol Identifier) is a filed of the VLAN tag. IEEE 802.1Q specifies the value of TPID to be 0x8100. This switch adopts the default value of TPID (0x8100) defined by the protocol. Other manufacturers use other TPID values (such as 0x9100 or 0x9200) in the outer tags of VLAN-VPN packets. To be compatible with devices coming from other manufacturers, this switch can adjust the TPID values of VLAN-VPN packets globally. You can configure TPID values by yourself. When 68