Weslo Summit St65 Owners Manual - Page 8
Conditioning, Guidelines.
 |
View all Weslo Summit St65 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 8 highlights
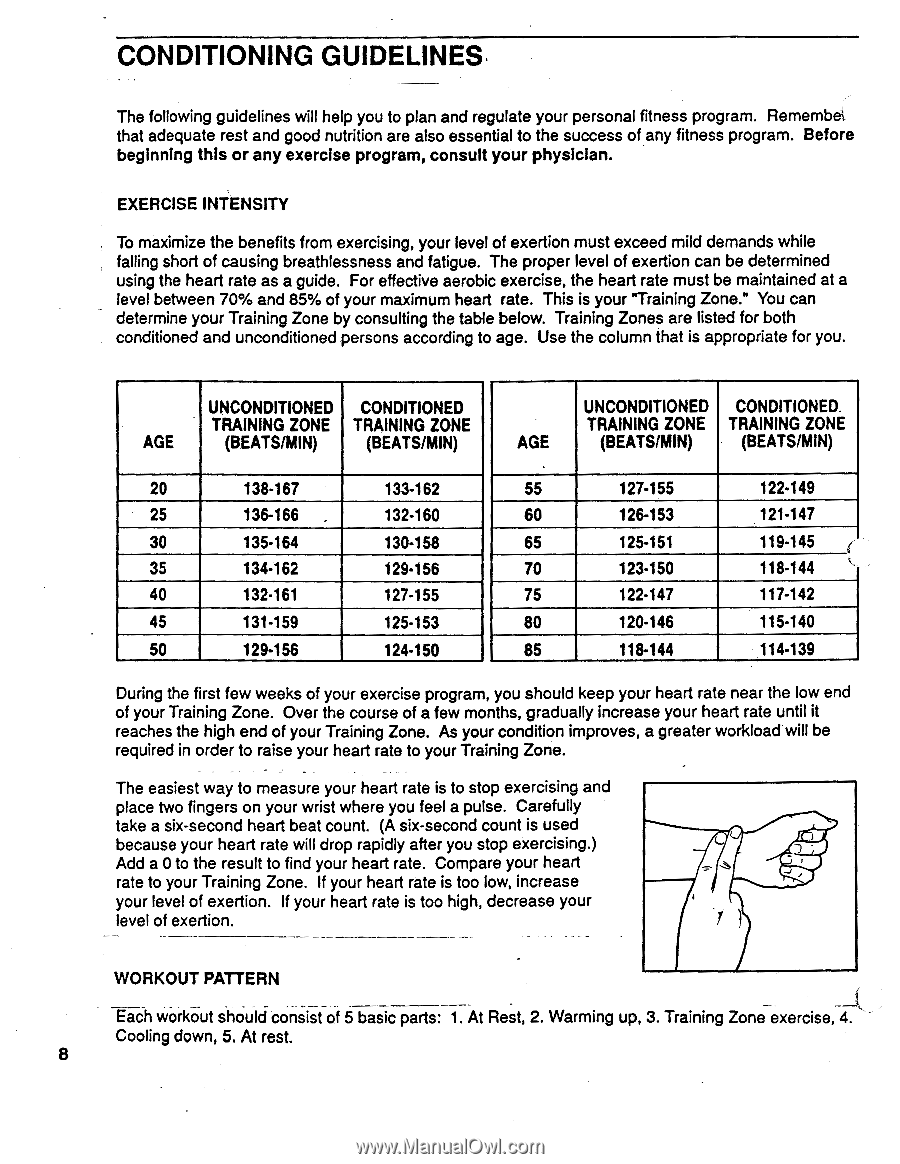
CONDITIONING GUIDELINES. The following guidelines will help you to plan and regulate your personal fitness program. Remembei that adequate rest and good nutrition are also essential to the success of any fitness program. Before beginning this or any exercise program, consult your physician. EXERCISE INTENSITY To maximize the benefits from exercising, your level of exertion must exceed mild demands while falling short of causing breathlessness and fatigue. The proper level of exertion can be determined using the heart rate as a guide. For effective aerobic exercise, the heart rate must be maintained at a level between 70% and 85% of your maximum heart rate. This is your "Training Zone." You can determine your Training Zone by consulting the table below. Training Zones are listed for both conditioned and unconditioned persons according to age. Use the column that is appropriate for you. UNCONDITIONED CONDITIONED TRAINING ZONE TRAINING ZONE AGE (BEATS/MIN) (BEATS/MIN) UNCONDITIONED CONDITIONED. TRAINING ZONE TRAINING ZONE AGE (BEATS/MIN) (BEATS/MIN) 20 138-167 133-162 25 136-166 . 132-160 30 135-164 130-158 35 134.162 129.156 40 132-161 127-155 45 131.159 125-153 50 129.156 124.150 55 127.155 60 126-153 65 125-151 70 123-150 75 122.147 80 120-146 85 118.144 122.149 121-147 119-145 118-144 117-142 115-140 114-139 During the first few weeks of your exercise program, you should keep your heart rate near the low end of your Training Zone. Over the course of a few months, gradually increase your heart rate until it reaches the high end of your Training Zone. As your condition improves, a greater workload will be required in order to raise your heart rate to your Training Zone. The easiest way to measure your heart rate is to stop exercising and place two fingers on your wrist where you feel a pulse. Carefully take a six-second heart beat count. (A six-second count is used because your heart rate will drop rapidly after you stop exercising.) Add a 0 to the result to find your heart rate. Compare your heart rate to your Training Zone. If your heart rate is too low, increase your level of exertion. If your heart rate is too high, decrease your level of exertion. WORKOUT PATTERN Each workout should consist of 5 basic parts: 1. At Rest, 2. Warming up, 3. Training Zone exercise, 4. Cooling down, 5. At rest. 8