ZyXEL G-110 User Guide - Page 33
Authentication Mode, 8.3 IEEE 802.1x, 8.4 WPA, EAP Authentication, Encryption
 |
View all ZyXEL G-110 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 33 highlights
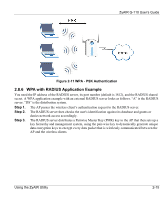
ZyAIR G-110 User's Guide 2.8.2 Authentication Mode The IEEE 802.11b standard describes a simple authentication method between the wireless stations and AP. Two authentication modes are defined: Open and Shared. Open authentication mode is implemented for ease-of-use and when security is not an issue. The wireless station and the AP do not share a secret key. Thus the wireless stations can associate with any AP and listen to any data transmitted plaintext. Shared authentication mode involves a shared secret key to authenticate the wireless station to the AP. This requires you to enable WEP encryption and specify a WEP key on both the wireless station and the AP. 2.8.3 IEEE 802.1x The IEEE 802.1x standard outlines enhanced security methods for both the authentication of wireless stations and encryption key management. Authentication can be done using an external RADIUS server. EAP Authentication EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) is an authentication protocol that runs on top of the IEEE802.1x transport mechanism in order to support multiple types of user authentication. By using EAP to interact with an EAP-compatible RADIUS server, an access point helps a wireless station and a RADIUS server perform authentication. The type of authentication you use depends on the RADIUS server and an intermediary AP(s) that supports IEEE802.1x. The ZyAIR supports EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS, EAP-PEAP and LEAP. Refer to the Types of EAP Authentication appendix for descriptions. For EAP-TLS and EAP-TTLS authentication types, you must first have a wired connection to the network and obtain the certificate(s) from a certificate authority (CA). A certificate (also called digital IDs) can be used to authenticate users and a CA issues certificates and guarantees the identity of each certificate owner. 2.8.4 WPA Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is a subset of the IEEE 802.11i security specification draft. Key differences between WPA and WEP are user authentication and improved data encryption. User Authentication WPA applies IEEE 802.1x and Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) to authenticate wireless clients using an external RADIUS database. Therefore, if you don't have an external RADIUS server you should use WPA-PSK (WPA -Pre-Shared Key) that only requires a single (identical) password entered into each access point, wireless gateway and wireless client. As long as the passwords match, a client will be granted access to a WLAN. Encryption WPA improves data encryption by using Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP), Message Integrity Check (MIC) and IEEE 802.1x. Using the ZyAIR Utility 2-13