Asus P5P43TD User Manual - Page 23
Memory configurations
 |
UPC - 610839171422
View all Asus P5P43TD manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
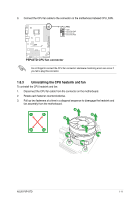
Page 23 highlights
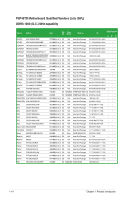
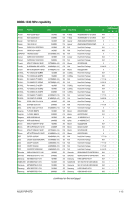
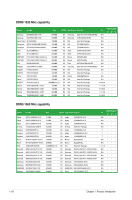
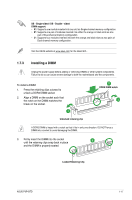
1.7.2 Memory configurations You may install 512MB, 1GB, 2GB, and 4GB unbuffered non‑ECC DDR3 DIMMs into the DIMM sockets. • You may install varying memory sizes in Channel A and Channel B. The system maps the total size of the lower-sized channel for the dual-channel configuration. Any excess memory from the higher-sized channel is then mapped for single-channel operation. • For dual-channel configuration, you can: - install two identical DIMMs in DIMM_A1 and DIMM_B1; or - install four identical DIMMs in all four slots; or - install one identical DIMM pair in DIMM_A1 and DIMM_B1 (black slots) and another identical DIMM pair in DIMM_A2 and DIMM_B2 (orange slots). • Always install DIMMs with the same CAS latency. For optimum compatibility, it is recommended that you obtain memory modules from the same vendor. • Due to the memory address limitation on 32-bit Windows® OS, when you install 4GB or more memory on the motherboard, the actual usable memory for the OS can be about 3GB or less. For effective use of memory, we recommend that you do any of the following: - Use a maximum of 3GB system memory if you are using a 32-bit Windows® OS. - Install a 64-bit Windows® OS when you want to install 4GB or more memory on the motherboard. • This motherboard does not support DIMMs made up of 256 megabits (Mb) chips or less. • This motherboard supports up to 16GB on Windows® XP Professional x64 and Windows® Vista x64 editions. You may install a maximum of 4GB DIMMs on each slot. • The default memory operation frequency is dependent on its Serial Presence Detect (SPD), which is the standard way of accessing information from a memory module. Under the default state, some memory modules for overclocking may operate at a lower frequency than the vendor-marked value. • For system stability, use a more efficient cooling system to support a full memory load (4 DIMMs) or overclocking conditions. ASUS P5P43TD 1-13