Casio FC-200V User Guide - Page 39
Independent Memory M - specification
 |
UPC - 079767167004
View all Casio FC-200V manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 39 highlights
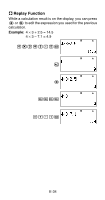
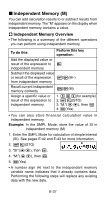
k Independent Memory (M) You can add calculation results to or subtract results from independent memory. The "M" appears on the display when independent memory contains a value. A Independent Memory Overview • The following is a summary of the different operations you can perform using independent memory. To do this: Perform this key operation: Add the displayed value or result of the expression to m independent memory Subtract the displayed value or result of the expression 1m(M-) from independent memory Recall current independent Sm(M) memory contents Assign a specific value or result of the expression to independent memory 1. 3+5(for example) 2. 1t(STO) 3. "M:"(fc), then E. 4. E(Yes) • You can also store financial calculation value in independent memory. Example: In the SMPL Mode, store the value of SI in independent memory (M) 1. Enter the SMPL Mode for calculation of simple interest (SI). See pages E-42 and E-43 for more information. 2. 1t(STO) 3. "SI"(fc), then E. 4. "M:"(fc), then E. 5. E(Yes) • A number sign (#) next to the independent memory variable name indicates that it already contains data. Performing the following steps will replace any existing data with the new data. E-37