Compaq dc7900 Technical Reference Guide: HP Compaq dc7900 Series Business Desk - Page 20
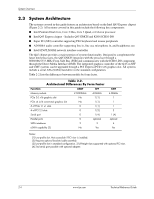
System Architecture, Table 2-2., Architectural Differences By Form Factor - cmt
 |
View all Compaq dc7900 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 20 highlights
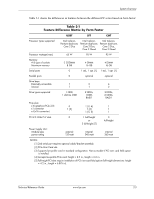
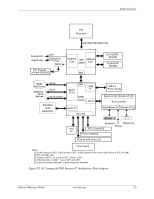
System Overview 2.3 System Architecture The systems covered in this guide feature an architecture based on the Intel Q45 Express chipset (Figure 2-2). All systems covered in this guide include the following key components: ■ Intel Pentium Dual-Core, Core 2 Duo, Core 2 Quad, or Celeron processor. ■ Intel Q45 Express chipset - Includes Q45 GMCH and 82801 ICH10-DO ■ Super I/O (SIO) controller supporting PS/2 keyboard and mouse peripherals ■ AD1884A audio controller supporting line in, line out, microphone in, and headphones out ■ Intel 82567LM GbE network interface controller The Q45 chipset provides a major portion of system functionality. Designed to complement the latest Intel processors, the Q45 GMCH integrates with the processor through a 800/1066/1333-MHz Front-Side Bus (FSB) and communicates with the ICH10-DO component through the Direct Media Interface (DMI). The integrated graphics controller of the Q45 on SFF and CMT systems can be upgraded through a PCI Express (PCIe) x16 graphics slot. All systems include a serial ATA (SATA) hard drive in the standard configuration. Table 2-2 lists the differences between models by form factor. Table 2-2. Architectural Differences By Form Factor Function USDT SFF Memory sockets 2 SODIMMs 4 DIMMs PCIe 2.0 x16 graphics slot No 1 [1] PCIe x4 (x16 connector) graphics slot No 1 [1] # of PCIe 1.1 x1 slots 0 1 [1] # of PCI 2.3 slots 0 1 [3] Serial port 0 1 [4] Parallel ports 0 optional SATA interfaces 2 3 eSATA capability [2] No Yes CMT 4 DIMMs 1 1 1 3 1 [4] optonal 4 Yes Notes: [1] Low-profile slot. Not accessible if PCI riser is installed. [2] Requires optional bracket/cable assembly. [3] Low-profile slot in standard configuration. 2 full-height slots supported with optional PCI riser. [4] 2nd serial port possible with optional adapter. 2-4 www.hp.com Technical Reference Guide