D-Link DCS-932L Product Manual - Page 57
Wireless Modes
 |
UPC - 790069351129
View all D-Link DCS-932L manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 57 highlights
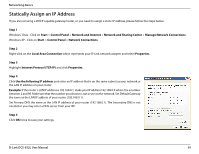
Wireless Basics Wireless Modes There are basically two modes of networking: • Infrastructure - All wireless clients will connect to an access point or wireless router. • Ad-Hoc - Directly connecting to another computer, for peer-to-peer communication, using wireless network adapters on each computer, such as two or more DCS-932L wireless network Cardbus adapters. An Infrastructure network contains an Access Point or wireless router. All the wireless devices, or clients, will connect to the wireless router or access point. An Ad-Hoc network contains only clients, such as laptops with wireless cardbus adapters. All the adapters must be in Ad-Hoc mode to communicate. D-Link DCS-932L User Manual 57

57
D-Link DCS-932L User Manual
Wireless Basics
There are basically two modes of networking:
•
Infrastructure
– All wireless clients will connect to an access point or wireless router.
•
Ad-Hoc
– Directly connecting to another computer, for peer-to-peer communication, using wireless network adapters on each computer,
such as two or more DCS-932L wireless network Cardbus adapters.
An Infrastructure network contains an Access Point or wireless router. All the wireless devices, or clients, will connect to the wireless router or
access point.
An Ad-Hoc network contains only clients, such as laptops with wireless cardbus adapters. All the adapters must be in Ad-Hoc mode to
communicate.
Wireless Modes