Dell EqualLogic FS7500 Dell EqualLogic FS7500 - Unified block and file storage - Page 9
Unified Scale-out Dell EqualLogic FS7500 Storage System,
 |
View all Dell EqualLogic FS7500 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 9 highlights
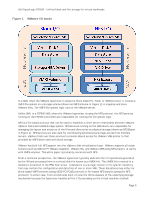
Dell EqualLogic FS7500 - Unified block and file storage for virtual workloads Figure 2. Unified Scale-out Dell EqualLogic FS7500 Storage System With the FS7500, you can scale both capacity and performance easily online; controllers and arrays are automatically discovered and added to the resource pool. When you need more storage capacity or I/O performance, you can add Dell EqualLogic PS Series storage arrays; these are automatically added to the storage pool and data is load-balanced across all the disks in the pool. To increase NAS performance, you can add FS7500 controllers; I/O is then spread across all available controllers to maximize performance. Whether you use the NFS or CIFS protocol, NAS performance scales in an almost linear fashion as you add controllers. While many traditional NAS systems have limitations on scalability and file system size based on architecture, the Dell EqualLogic FS7500 has no such restrictions. It can scale to the limit of the backend storage arrays in a single namespace; currently tested up to 509 TB of usable NAS space. This means you can surpass the limitations of traditional file systems, providing contiguous space for even your most demanding applications. NAS datastores can even simplify the implementation and management of a VMware virtual environment because NAS storage volumes can be simpler to deploy and manage than traditional SAN volumes. The NAS device is responsible for the provisioning and allocation of the storage. The hypervisor essentially maps a network drive to the NAS device; much in the same way users would connect to their home folders. This greatly simplifies the administrative tasks required by virtualization administrators because connecting an ESX host to a NAS-based storage requires no specialized training in storage administration. In addition, NAS-based datastores in a VMware environment provide nearly all the major features of block-based storage volumes, but without the complexities involved in managing a traditional SAN storage network. Page 7