Dell PowerConnect 2708 User's Guide - Addendum - Page 11
Configuring Class of Service (CoS), Strict Priority, Weighted Round Robin
 |
View all Dell PowerConnect 2708 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 11 highlights
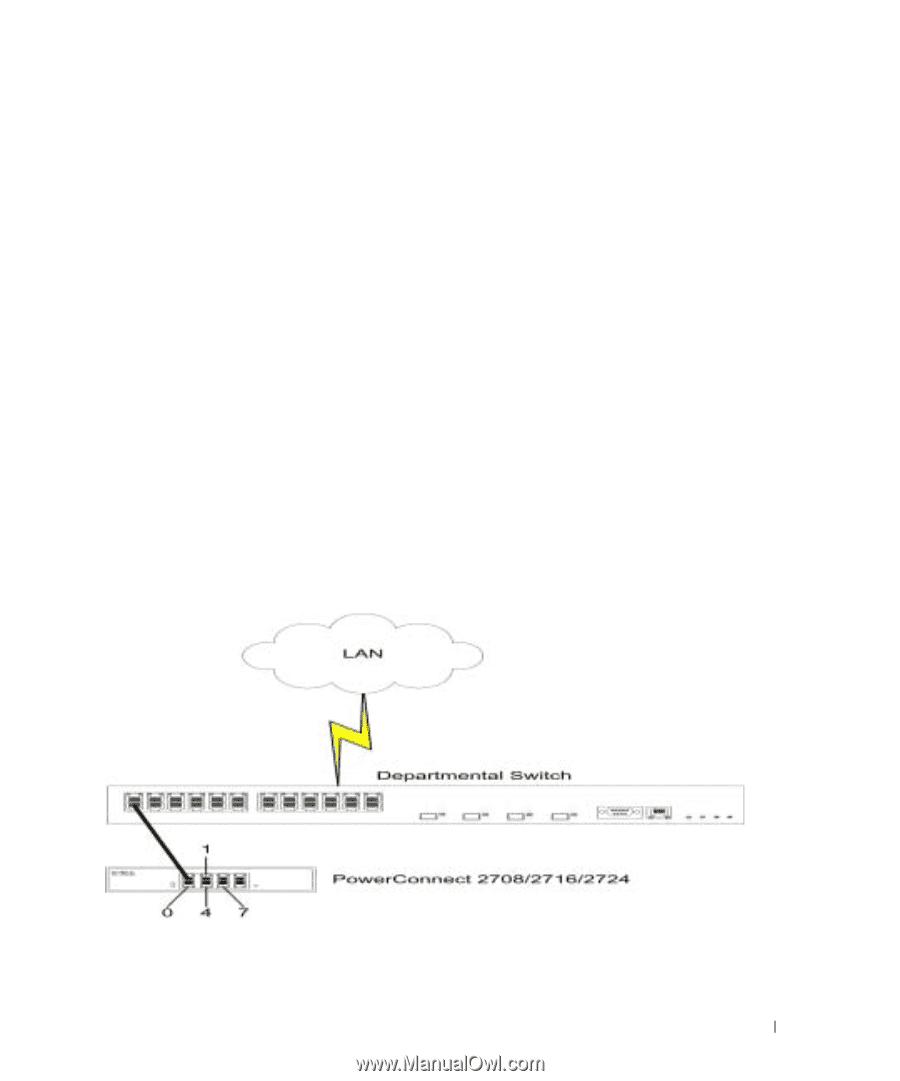
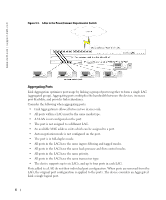
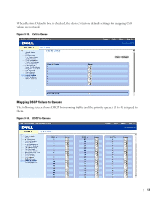
Configuring Class of Service (CoS) The underlying mechanism of Class of Service (CoS) is the concept of queues. After packets are assigned to a specific egress queue, CoS services can be assigned to the queue(s). The PowerConnect 2708/2716/2724 system supports four queues per port for service priorities, where queue 0 is the lowest priority and queue 3 is the highest priority. For each logical group of priorities defined by the user, two priority levels are defined. Egress queues are configured with a scheduling scheme by one of the following methods: Strict Priority - Ensures that time-sensitive applications are always forwarded. Strict Priority (SP) allows the prioritization of mission-critical, time-sensitive traffic over less time-sensitive applications. For example, under Strict Priority, voice over IP traffic can be prioritized so the IP traffic is forwarded before FTP or e-mail traffic. Weighted Round Robin - Ensures that a single application does not dominate the device forwarding capacity. Weighted Round Robin (WRR) forwards entire queues in a Round Robin order. All queues can participate in WRR, with expect SP queues. SP queues are serviced before WRR queues. If the traffic flow is minimal, and SP queues do not occupy the whole bandwidth allocated to a port, the WRR queues can share the bandwidth with the SP queues. Ensuring the remaining bandwidth is distributed according to the weight ratio. If WRR is selected, the following weights are assigned to the queues: 1, 2, 4, 8. The following figure illustrates the concept of CoS priority queues managed by the device. In this scenario, priorities are assigned to untagged incoming packets, per port. Figure 9-11. CoS Priority Queues 11