Epson 3170 Technical Brief (Scanners) - Page 6
Dynamic Range, Focus Method, Fixed Focus, Dual-Focus mechanism, AutoFocus optics system - manual
 |
UPC - 010343846630
View all Epson 3170 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 6 highlights
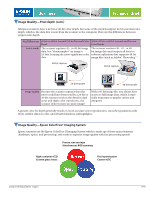
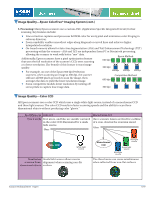
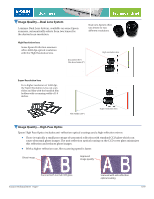
Image Quality-Dynamic Range Dynamic range measures the difference between the lightest highlights and darkest shadows that a scanner can perceive (on a scale of 3.0 to 4.0). The maximum density rating is referred to as Dmax. A dynamic range measurement is important for designers who scan transparent media (such as slides, transparencies, and negatives) because the media itself generally has a dynamic range of 3.2. Reflective media, such as a photograph, generally does not have a dynamic range greater than 2.0. A high dynamic range results in scanned images with superior detail in highlights and in shadows- especially when scanning transparent media. Superior detail in highlights Superior detail in shadows Image Quality-Focus Method Epson scanners use a fixed focus system, AutoFocus optics system, or a Dual-Focus mechanism. 1. Fixed Focus: With this type of focus system, the lens is set to record everything sharply from a fixed distance-from the lens to the glass scanning bed. The Epson Perfection and GT series scanners use a fixed focus optics system. The newest Epson scanners have a fixed focal point just above the surface of the glass for optimized film scanning. 2. AutoFocus optics system: Epson highest-end graphic Epson automatic/manual focus arts scanners use an AutoFocus optics system that can be used in AutoFocus mode or manual mode. This system offers these benefits: The Epson manual/automatic focus optics system gives you precised sharpness control, especially when scanning three-dimensional objects and transparencies. With three-dimensional images, you can pick your point of focus so that background items are captured with sharp detail, as shown in the glove and towel in the images to the right. For super sharpness when scanning transparencies or slides mounted in holders, you can set the focus to compensate for the 2.5mm distance between the glass and the slide. Standard fixed focus 3. Dual-Focus mechanism: One of the Epson Expression series scanners uses a Dual-Focus mechanism. When using the scanner's custom film holders to scan transparent media, you can set the scanner's focal distance to compensate for the 2.5mm distance between the glass and the media. This method eliminates the "Newton Ring" problem that plagues less sophisticated scanners. Newton Rings are the circular rainbowcolored patterns that appear in a scanned image, caused by surface tension. This effect is similar to the rainbows that appear in soap bubbles. Scanner Technical Brief-Page 6 6/07