HP 127695-B21 Smart Array Controller Technology: Drive Array Expansion and Ext - Page 7
RAID migration, Smart Array Controller User, Guide, Assessing RAID ADG vs. RAID 5 vs. RAID 1+0
 |
UPC - 743172872142
View all HP 127695-B21 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 7 highlights
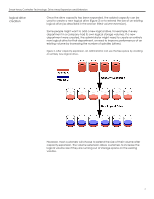
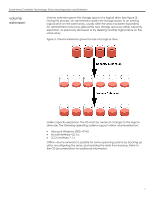
Smart Array Controller Technology: Drive Array Expansion and Extension RAID migration Administrators may perform volume extension in order to increase raw data storage capacity, to improve performance by increasing the number of spindles in a logical drive volume , or to change fault-tolerance (RAID) configurations. With ACU or ACU-XE, an administrator can reconfigure a logical drive to a new RAID level online, without disrupting system operation or causing data loss. The following situations would require additional drive space: changing RAID 0 to RAID 1, 5, or RAID ADG; or changing RAID 5 or RAID ADG to RAID 1. Table 1 summarizes the RAID levels and the amount of space required for each type of fault tolerance. table 1. Summary of RAID methods Usable drive space* Usable drive space formula Minimum number of drives Tolerant of single drive failure? Tolerant of multiple simultaneous drive failures? Read performance Write performance Relative cost RAID 0 (striping) 100% n 1 No No High High Low RAID 1 (mirroring) 50% RAID 5 (distributed data guarding) 67% to 93% n/2 (n-1)/n 2 3 Yes Yes If failed drives not mirrored to each other High No High Medium Low High Medium RAID ADG (advanced data guarding) 50% to 96% (n-2)/n 4 Yes yes High Low medium * The values for usable drive space are calculated assuming a maximum of 14 physical drives of the same capacity (or a maximum of 56 for RAID ADG) with no online spares. HP recommends that these maximum figures (excluding any allowable online spares) are not exceeded when configuring a drive array, due to the increased likelihood of logical drive failure with more hard drives. For more information about RAID levels, refer to the Smart Array Controller User Guide, or the document titled Assessing RAID ADG vs. RAID 5 vs. RAID 1+0. Both are available from the smart array controller webpage.5 5 The Smart Array controller webpage is available at the following URL: http://www.compaq.com/products/servers/proliantstorage/arraycontrollers/docs/index.html 7