HP 6120G/XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches Advanced Traffic Management - Page 168
Troubleshooting MSTP Operation, Table 4-2.
 |
View all HP 6120G/XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 168 highlights
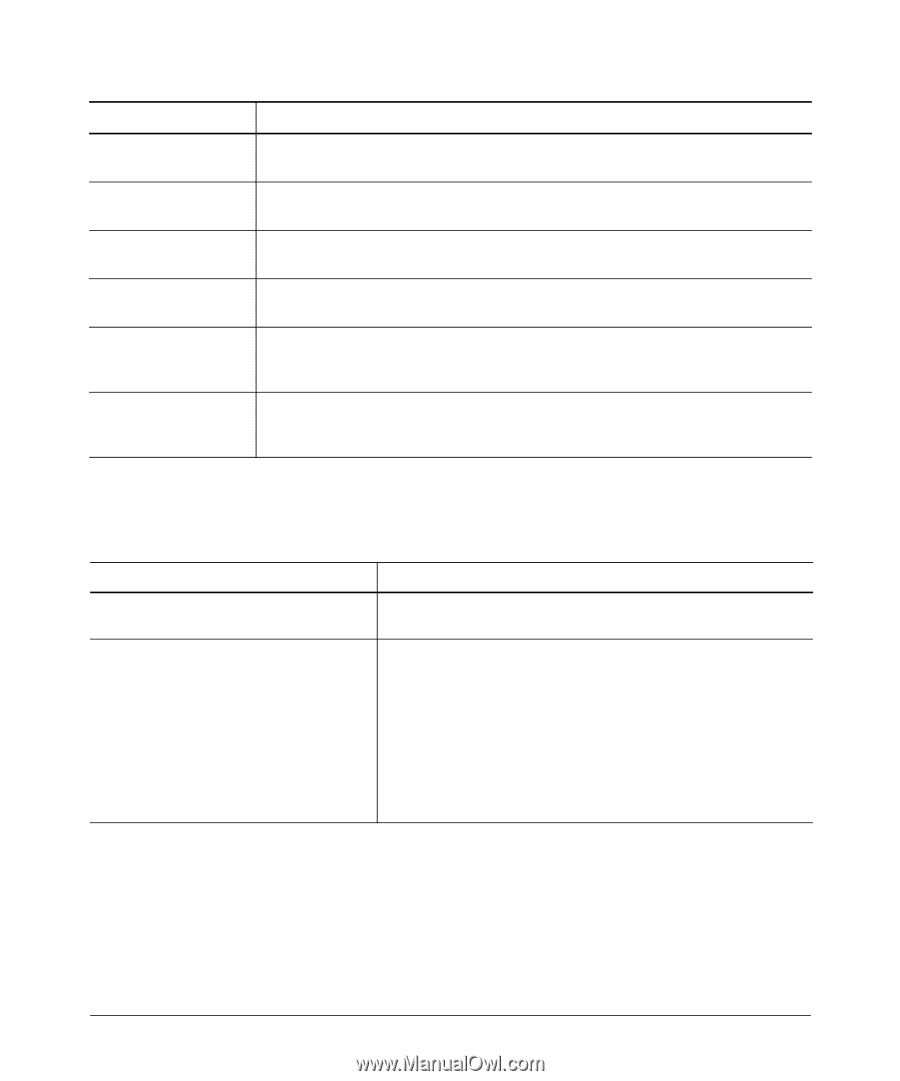
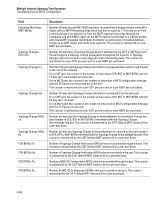
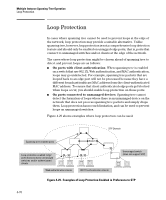
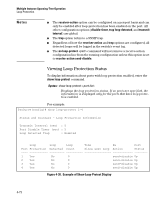
Multiple Instance Spanning-Tree Operation Troubleshooting an MSTP Configuration Field RST BPDUs Tx RST BPDUs Rx MST BPDUs Tx MST BPDUs Rx MSTI MSGs Tx MSTI MSGs Rx Description Number of (802.1w) RST BPDUs that are transmitted through the port. This counter is maintained by the CIST (default MST instance 0) on a per-port basis. Number of (802.1w) RST BPDUs that are received on the port. This counter is maintained by the CIST (default MST instance 0) on a per-port basis. Number of (802.1s) MST BPDUs that are transmitted through the port. This counter is maintained by the CIST (default MST instance 0) on a per-port basis. Number of (802.1s) MST BPDUs that are received on the port. This counter is maintained by the CIST (default MST instance 0) on a per-port basis. Number of times that a configuration message for a specific MSTI was encoded in (802.1s) MST BPDUs that are transmitted through the port. This counter is maintained on a per-MSTI per-port basis. Number of times that the MSTI detected a configuration message destined to the MSTI in (802.1s) MST BPDUs received on the port. This counter is maintained on a per-MSTI perport basis. Troubleshooting MSTP Operation Table 4-2. Troubleshooting MSTP Operation Problem Possible Cause Duplicate packets on a VLAN, or packets not The allocation of VLANs to MSTIs may not be identical among all arriving on a LAN at all. switches in a region. A switch intended to operate in a region does not receive traffic from other switches in the region. An MSTP switch intended for a particular region may not have the same configuration name or region revision number as the other switches intended for the same region. The MSTP configuration name (spanningtree config-name command) and MSTP configuration revision number (spanning-tree config-revision command) must be identical on all MSTP switches intended for the same region. Another possible cause is that the set of VLANs and VLAN ID-to-MSTI mappings (spanning-tree instance vlan command) configured on the switch may not match the set of VLANs and VLAN ID-to-MSTI mappings configured on other switches in the intended region. 4-69