HP 800 HP DLPI Programmer's Guide - Page 30
DLPI Services,
 |
View all HP 800 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 30 highlights
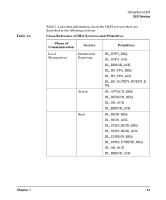
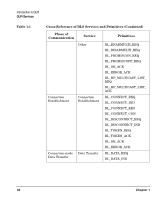
Introduction to DLPI DLPI Services DLPI Services The various features of the DLPI interface are defined in terms of the services provided by the DLS provider and the individual primitives that may flow between the DLS user and DLS provider. HP DLPI supports two of the three modes of service: connection and connectionless. HP DLPI does not support acknowledged connectionless service. The connection mode is circuit-oriented and enables data to be transferred over an established connection in a sequenced manner. The connectionless mode is message-oriented and supports data transfer in self-contained units with no logical relationship required between units. DLPI also includes a set of local management functions that apply to all modes of service. DLPI supports the XID and TEST services that appear in the following table. The DLS user can issue an XID or TEST request to the DLS provider. The provider will transmit an XID or TEST frame to the peer DLS provider. On receiving a response, the DLS provider sends a confirmation primitive to the DLS user. On receiving an XID or TEST frame from the peer DLS provider, the local DLS provider sends up an XID or TEST indication primitive to the DLS user. The user must respond with an XID or TEST response frame to the provider. In addition, raw mode service is now supported. Raw mode allows the DLS user to send and receive packets with complete LLC and MAC headers. Security Containment With the Security Containment product version B.11.23.01 or later, HP DLPI will allow raw mode service only for users with PRIV_NETRAWACCESS privilege. See "Fine-grained Privileges with Security Containment Release" on page 17 for more details. 30 Chapter 1