HP Integrity Superdome 2 8/16 HP Integrity Superdome 2 User Service Guide - Page 91
A Utilities, UEFI, UEFI Shell and HP POSSE commands
 |
View all HP Integrity Superdome 2 8/16 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 91 highlights
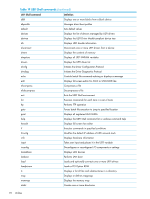
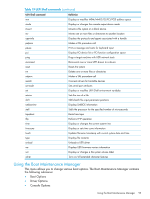
A Utilities UEFI UEFI is an OS and platform-independent boot and preboot interface. UEFI resides between the OS and platform firmware, allowing the OS to boot without having details about the underlying hardware and firmware. UEFI supports boot devices, uses a flat memory model, and hides platform and firmware details from the OS. NOTE: Unified EFI Forum, Inc. defines the specification used to implement UEFI. POSSE is an HP extension to UEFI, which provides a common user interface architecture to better serve HP customers, service, and manufacturing. UEFI consolidates boot utilities similar to those found in PA-RISC-based servers, such as the BCH, and platform firmware into a single platform firmware. UEFI allows the selection of any UEFI OS loader from any boot medium that is supported by UEFI boot services. An UEFI OS loader supports multiple options on the user interface. UEFI supports booting from media that contain an UEFI OS loader or an UEFI-defined server partition. An UEFI-defined system partition is required by UEFI to boot from a block device. The UEFI boot manager loads UEFI applications (including the OS first-stage loader) and UEFI drivers from an UEFI-defined file system or image loading service. NVRAM variables point to the file to be loaded. These variables contain application-specific data that is passed directly to the UEFI application. UEFI variables provide system firmware a boot menu that points to all the operating systems; even multiple versions of the same operating systems. The UEFI boot manager allows you to control the server's booting environment. Depending on how you have configured the boot options, after the server is powered up, the boot manager presents you with different ways to bring up the server. For example, you can boot to the UEFI shell, to an operating system located on the network or residing on media in the server, or the Boot Maintenance Manager. See "Using the Boot Maintenance Manager" (page 93) for more information. UEFI Shell and HP POSSE commands For more information about these commands, enter helpcommand at the UEFI Shell prompt. Table 19 UEFI Shell commands UEFI Shell command ? alias attrib autoboot bcfg boottest cd cls comp conconfig connect cp date Definition Displays the UEFI Shell command list or verbose command help Displays, creates, or deletes UEFI Shell aliases Displays or changes the attributes of files or directories Sets or displays autoboot timeout and retries Displays or modifies the driver/boot configuration Turns specific speedyboot bits on or off Displays or changes the current directory Clears standard output and optionally changes background color Compares the contents of two files Configures consoles and sets or displays primary operating system console Connects one or more UEFI drivers to a device Copies one or more files or directories to another location Displays or changes the current system date UEFI 91