HP ML530 Optimizing facility operation in high density data center environment - Page 6
P-state management, Efficient practices for servers and enclosures - proliant bios
 |
UPC - 720591250669
View all HP ML530 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 6 highlights
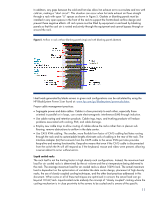
Table2. P-states of the Intel Quad-Core 2.66-GHz processor P-state Description Core Frequency Pmax Pmin Maximum performance Minimum power 2.66 GHz 2.0 GHz Approximate Core voltage 1.2 VDC 1.0 VDC P-state management IT administrators can control processor P-states by one of two basic methods: through the operating system (OS) with the use of a driver, or more directly through firmware in the BIOS ROM (Figure 2). Figure 2. Methods for controlling processor P-states OS Control Mode OS Driver System ROM Hardware Registers HP Dynamic and Static control modes System ROM Hardware Registers An OS-based control method requires an OS upgrade and driver installation on any server where Pstate management is desired. A ROM-based solution, however, provides P-state control at power-up, requires no software loading or upgrade, and can operate on systems running an OS that does not support P-state management. HP Power Regulator for ProLiant servers is an example of OSindependent, power management. This HP hardware/software implementation enables a system administrator to manage processor power consumption and system performance in either static or dynamic modes. Mare information about the Power Regulator for ProLiant servers can be found at www.hp.com/servers/power-regulator. Efficient practices for servers and enclosures The HP product line includes dual-processor and quad-processor server blades that can be installed in the same rack-mounted enclosure, interconnected, and easily managed. This high-density server technology lowers the operating cost per processor by reducing management expenses and the requirements for floor space. Understanding server power utilization and heat generation IT equipment manufacturers typically provide power and heat load information in their product specifications. HP provides a Rack/Site Installation Preparation Utility to assist customers in approximating the power and heat load per rack for facilities planning. The Site Installation Preparation Utility uses the power calculators for individual platforms so that customers can calculate the full environmental effect of racks with varying configurations and loads. This utility can be downloaded from http://h30099.www3.hp.com/configurator/calc/Site%20Preparation%20Utility.xls. 6