HP NetServer LP 2000r 8-way Systems Enable Enterprise Applications - Page 4
hp-ux, linux
 |
View all HP NetServer LP 2000r manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 4 highlights
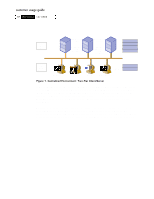
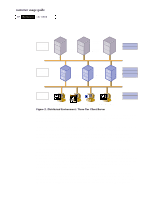
FXVWRPHUýXVDJHýJXLGH +3ý 1HW6HUYHUý /;Uýåèíí Tier Two Servers ERP Central Server Application and Database Consolidated Servers Multiple Applications and Databases Data Management Business Logic Device Management transport Tier One Clients hp-ux linux Windows 95/98 UNIX MAC OS PC Clients Windows NT/2000 transport Presentation (KIWTG"30"%GPVTCNK\GF"'PXKTQPOGPV

FXVWRPHU XVDJH JXLGH
4
+3
1HW6HUYHU
/;U °L±±
Windows NT/2000
UNIX
hp-ux
hp-ux
MAC OS
Consolidated
Servers
Multiple
Applications
and
Databases
Tier
Two
Servers
PC
Clients
Tier
One
Clients
transport
Presentation
Data Management
Business Logic
transport
Device Management
ERP Central
Server
Application
and
Database
Windows 95/98
linux
linux
(KIWTG
30
%GPVTCNK\GF ’PXKTQPOGPV
<
6YQ
/
6KGT %NKGPV
1
5GTXGT
In the centralized environment, the application presentation component runs on the client
with the application business logic and the database management software running on a
server system, competing for server resources. In a distributed environment with 3-tier
topologies, a database is on the third tier (the database server) and one or more
application servers comprise the second tier. Client systems are the first tier in either
arrangement.
Distributed environments can support several times the number of active users over a
centralized system, depending upon the power of the chosen servers. Clearly, the
distributed environment requires more hardware but the scalability in terms of the number
of users supported or the potential transaction throughput offsets the complexity and the
cost.