HP NetServer LXr Pro8 Server Controllers and Mass Storage Devices - Page 8
Disk Array, or Fibre Channel controllers may be added. The HP NetServer website
 |
View all HP NetServer LXr Pro8 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 8 highlights
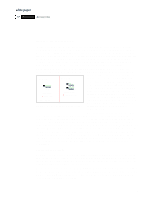
ZKLWHýSDSHU +3ý 1HW6HUYHUý $FFHVVRULHV Hard Disk Drives SCSI hard disk drives are available in a variety of capacities from 4 to 18 GB, with higher capacity drives (36 GB) planned for mid-1999. HP offers drives at two rotational speeds: 7200 and 10,000 rpm. The higher speed drive offers shorter seek times and improved system performance. Drives are available for either internal or external storage systems. HP offers two versions of external storage: rack-optimized or pedestal/standalone configurations. HP's position as a leading server vendor gives the company considerable leverage with leading drive vendors. HP has close relationships with these drive vendors, allowing HP to work with them on new drive technologies and standards, to thoroughly test these technologies with HP NetServer hardware and software, and to bring them to market in cost-effective and timely ways. As an example, HP offers proactive warranty replacement on drives, meaning that the company will replace them for you if HP server management software indicates a problem-even if a failure has not yet occurred. Current areas of cooperation with drive vendors include both higher capacity and faster drives, enhanced drive connection mechanisms, and better availability and management features. Performance improvements include 10K RPM drives and low voltage differential (Ultra2) SCSI technology. HP NetServers offers standard SCSI controllers in all server systems. Additional SCSI, Disk Array, or Fibre Channel controllers may be added. The HP NetServer website provides lists of tested controller cards, organized by platform, as well as more information about each of the controller products. HP NetServer RAID Configurations RAID can be implemented in software or hardware. Software-based RAID uses host CPU cycles and system memory adding processing overhead that may impact system performance. Disk array controllers (DAC), the hardware solution, transfer the overhead from the host CPU to specialized hardware that typically performs better than the software RAID. The DAC can be programmed to support a hot spare drive configuration. With this X bad drive is replaced Hot Spare arrangement, if a drive should fail, the system can automatically begin rebuilding to the hot spare drive. See Figure 4 for an explanation of the differences between a Hot Swap array controller rebuilds data hot swap and a hot spare configuration. There are several RAID levels to choose from whether the implementation be Figure 4. Hot Swap versus Hot Spare with software or hardware. Five levels (1 through 5) were defined when the RAID concept was first proposed in 1988 by three academics from the University of California at Berkeley as a way to organize and protect stored data. Additional levels have since been developed to enhance performance and data redundancy. Hewlett-Packard NetRAID family controllers offer a choice of seven 8