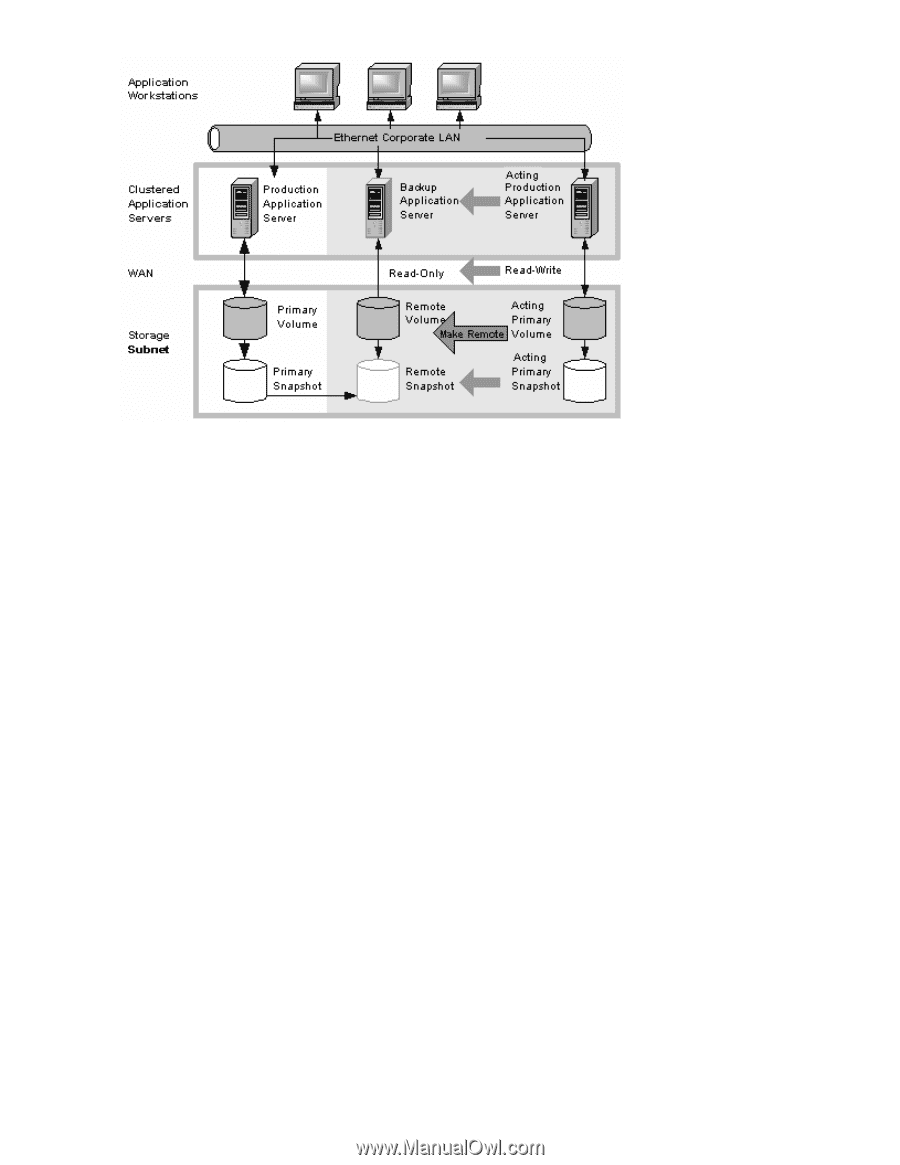
HP P4000 9.0 HP StorageWorks P4000 Remote Copy User Guide - Page 46
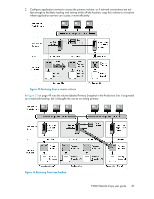
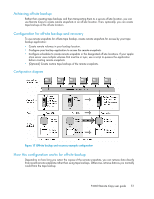
Best practices, Remote snapshots with volume replication, Example configuration - data protection
 |
View all HP P4000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 46 highlights
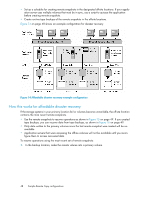
Figure 12 High availability configuration during failback . Best practices Remote snapshots with volume replication Use remote snapshots in conjunction with local, synchronous volume replication, known as Network RAID. Using remote snapshots alone, any data written to the primary volume since the most recent remote snapshot was created will be unavailable if the primary volume is unavailable. However, you can lessen the impact of primary volume failure by using Network RAID. Network RAID allows you to create up to four copies of a volume on the same cluster of storage systems as the primary volume. The only limitation is that the cluster must contain at least as many storage systems as replicas of the volume. Replicating the volume within the cluster ensures that if a storage system in the cluster goes down, replicas of the volume elsewhere in the cluster will still be available. For more information about Network RAID and data protection levels, see the chapter "Provisioning Storage" in the HP StorageWorks P4000 SAN Solution user guide. Example configuration Figure 10 on page 44 uses three storage systems per cluster. However, this scenario can use any number of storage systems. For information about creating clusters and volumes, see the HP StorageWorks P4000 SAN Solution user guide. • In the production location, create a management group and a cluster of three storage systems. • Create volumes on the cluster and set the data protection level to Network RAID-10. • Configure the production application server to access the primary volume via iSCSI. • In the backup location, create a second management group and a cluster of three storage systems. • Create a schedule for making remote snapshots of the primary volume. See "Scheduling remote snapshots" on page 29. 46 Sample Remote Copy configurations