HP ProLiant DL360e Implementing Microsoft Windows Server 2008 on HP ProLiant s - Page 5
Read-Only Domain Controllers, Networking requirements, TCP/IP, NDIS 6.0, IPv6
 |
View all HP ProLiant DL360e manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 5 highlights
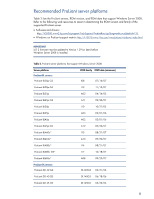
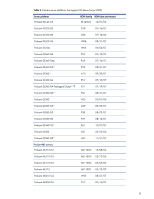
Read-Only Domain Controllers Windows Server 2008 introduces a new type of domain controller (DC), the read-only domain controller (RODC). This DC hosts read-only partitions of the Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS) database. An RODC provides a secure solution for DC deployments to remote sites that require fast and reliable authentication but do not necessarily have adequate physical security for the deployed servers. Additional information is available on the Microsoft website: http://technet2.microsoft.com/windowsserver2008/en/servermanager/activedirectorydomainservice s.mspx. Networking requirements TCP/IP Microsoft has updated the TCP/IP stack in Windows Server 2008. For more information on the next generation TCP/IP stack in Windows Server 2008, visit the Microsoft website: www.microsoft.com/technet/community/columns/cableguy/cg0905.mspx. NDIS 6.0 NDIS 6.0 is the next major version of the Network Driver Interface Specification. HP has updated the Windows Server 2008-capable network adapter drivers to meet the NDIS 6.0 requirements. A list of supported network adapters may be found in Table 5. For more information on NDIS 6.0, visit the Microsoft website: http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms795192.aspx. IPv6 Windows Server 2008 provides support for the next generation TCP/IP protocol stack known as Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6). Administrators should be aware that IPv6 support is enabled by default in a Windows Server 2008 installation. It cannot be uninstalled but may be disabled. For more information on IPv6, visit the Microsoft website: http://www.microsoft.com/technet/community/columns/cableguy/cg1005.mspx. Windows Hardware Error Architecture (WHEA) Windows Hardware Error Architecture is a new feature added to Windows Server 2008 that provides a common infrastructure for hardware errors on Windows platforms. The initial implementation of WHEA focuses on platform hardware devices, including processor, memory, cache, and system interconnects such as PCI, PCI-X, and PCI Express. Peripheral device errors remain under the control of their respective device drivers. WHEA provides several benefits: • A generic error source discovery mechanism • A common hardware error record format and error handling flow • A persistence mechanism for preserving error records • A hardware error event tracking model based on Event Tracing for Windows (ETW) Not all HP servers that support Windows Server 2008 will be WHEA compatible. Table 2 lists the WHEA-capable ProLiant servers. HP has updated the following deliverables in support of WHEA: • System ROMs for specific ProLiant server platforms planned for WHEA support (see Table 2) • iLO firmware (version 1.42 or later) • iLO 2 Management Controller Driver for Windows Server 2008 [hpqilo2.sys, Version 1.5 (or later)] 5