HP ProLiant SL335s HP ProLiant SL6000 Scalable System technology, 2nd Edition - Page 8
Memory technologies, Unbuffered and registered DIMMs - g7 server
 |
View all HP ProLiant SL335s manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 8 highlights
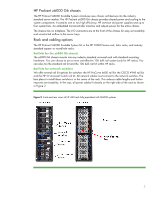
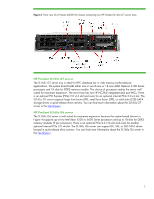
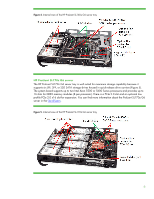
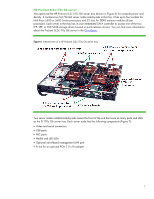
Figure 7. Front view of two ProLiant z6000 G6 chassis, each containing two HP ProLiant SL2x170z G6 server trays Memory technologies SL6000 server trays use DDR3 memory. You can control all processor function options, including memory mirroring and memory channel interleaving. You use the ROM-based setup utility (RBSU) for G6 or G7 servers to do that. You will find details about DDR3 memory in the HP paper titled "Memory technology evolution: an overview of system memory technologies." Unbuffered and registered DIMMs DDR3 DIMMs are available as both Unbuffered (UDIMMs) and Registered (RDIMMs). Both UDIMMs and RDIMMs support error-correcting code (ECC). There are three types of DDR3 memory: • PC3-8500R (RDIMM)-1066 or 800 megatransfers per second (MT/s) data rate, depending on the memory configuration and processor • PC3-10600E (UDIMM)-1333, 1066, or 800 MT/s data rate, depending on the memory configuration and processor • PC3-10600R (RDIMM)-1333, 1066, or 800 MT/s data rate, depending on the memory configuration and processor You cannot mix UDIMM and RDIMM memory within a single server tray. UDIMM configurations have a maximum of two UDIMMs per memory channel because the memory controller must drive the address and command signals to each DRAM chip on a channel. This results in a 24 GB maximum configuration. UDIMMs are typically less expensive than RDIMMs because UDIMMs require fewer components. RDIMM configurations can provide larger memory capacity because the memory controller only drives the address and command signals to a single register chip. This reduces the electrical load on the 8