HP ProSignia 200 Performance Analysis and Tuning of Raptor's Eagle NT 3.06 Fir - Page 6
Servers, FTP requests, HTTP requests, Clients, server01, server02, server03, server04, Server05,
 |
View all HP ProSignia 200 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 6 highlights
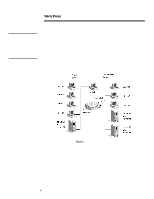
278A/0497 WHITE PAPER (cont.) ... The security rule set contains the following rules using FTP ports (20,21), HTTP port (80) protocols: • Private to Private, Private to Hostile, and Private to DMZ - Allow All • Hostile/DMZ to Private - Allow only to specified servers. Logging affects the firewall throughput; therefore moderate logging is used. This logs all connections, spoof detection messages, TCP syn/fin messages, and connect rejection messages. The test methodology uses 6 virtual servers from 3 physical servers and 1 to 72 virtual clients on 8 physical clients. Virtual clients are administered from one of the physical clients known as the control machine. Each virtual client makes 100 request for FTP GET and HTTP GET transfers to the 6 virtual servers. HTTP/CGI requests were also available but not used because HTTP/CGI requests could skew the totals due to web server processing of CGI requests. Percentages used to determine the amount of traffic the virtual clients send to the virtual servers is a configurable item for the methodology. For configurations used in test runs contained in this paper, each virtual server receives the percentages of HTTP and FTP requests from the virtual clients as listed in Table 1. Servers % FTP requests % HTTP requests server01, server03, server05 10 90 server02, server04, server06 90 10 Table 1: Test Bed Protocol Percentage Server requests percentages are the same for all sets of virtual clients used. Also, the setup places server01 and server02 in the Private Zone and server03 through server06 in the DMZ/Hostile Zone. This setup follows the procedures used in previous NSTL tests. The amount of requests per virtual client is also configurable. In practice, using 100 requests per virtual client and using up to 72 virtual clients produces a good load on the client systems and pushes a high amount of traffic through the network. Therefore, using 72 virtual clients was adopted as the maximum number of virtual clients used in the test runs. In all test runs (eight per hardware configuration), the number of virtual clients was 1, 12, 24, 32, 36, 48, 60, and 72. This approach in the number of virtual clients used shows how the firewall reacts under progressively heavier loads. The percentages of servers that are hit from each of the physical clients are also configurable items as presented in Table 2. Clients server01 server02 server03 server04 Server05 server06 client01 - 2.4% client05 2.4% 23.8% 23.8% 23.8% 23.8% client06 - 40% 40% 5% 5% 5% 5% client08 Table 2: Percentage of Servers hit by Clients The file types used for transactions for the benchmark were ZIP files for FTP transfers and HTML and GIF files for HTTP transactions. The sizes of the files for FTP are 32, 64, 128, and 256 kilobytes. HTTP file sizes, with one directory depth, were 1, 2, 4, 8, 10, 20, 40, and 80 kilobytes for HTML files and 512 bytes, 1, 2, 4, 10, 26, 52, 104, and 208 kilobytes for GIF files. All files were automatically generated using the NSTL configuration toolkit. 6