HP Xw6400 HP Workstations RAID Primer - Page 3
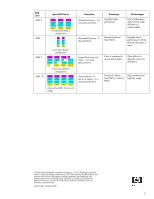
Level, Typical RAID Layout, Description, Advantages, Disadvantages - how to set up raid
 |
UPC - 882780645493
View all HP Xw6400 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 3 highlights
RAID Level RAID 0 RAID 1 RAID 5 RAID 10 Typical RAID Layout D1[1] D1[2] D1[3] D2[1] D2[2] D2[3] D3[1] D3[2] D3[3] D4[1] D4[2] D4[3] A three drive RAID 0 configuration D1 D1 D2 D2 D3 D3 D4 D4 A two drive RAID 1 configuration D1[1] D1[2] D1[3] P1 D2[1] D2[2] P2 D2[3] D3[1] P3 D3[2] D3[3] P4 D4[1] D4[2] D4[3] A four drive RAID 5 configuration D1[1] D2[1] D3[1] D4[1] D1[2] D2[2] D3[2] D4[2] D1[1] D2[1] D3[1] D4[1] D1[2] D2[2] D3[2] D4[2] A four drive RAID 10 mirror of stripes Description Striped Disk Array - 2 or more physical drives Mirrored Disk Array - 2 physical drives Striped Disk Array with Parity - 3 or more physical drives Stripe of Mirrors or Mirror of Stripes - 4 or more physical drives Advantages Typically higher performance Disadvantages Lack of redundancy implies that a single disk failure is unrecoverable More fault tolerant than RAID 0 Typically slower performance; half the physical disk space is used Parity is employed to ensure data integrity Often difficult to rebuild in case of a disk failure More fault tolerant than RAID 0, similar to RAID 1 High overhead and high disk usage © 2006 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein. 439276-001, October 2006 3