HP Xw6400 Software RAID in Linux Workstations - Page 5
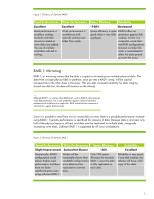
RAID-1: Mirroring, Read Performance, Space Efficiency, Reliability
 |
UPC - 882780645493
View all HP Xw6400 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 5 highlights
Figure 1. Efficiency of Software RAID-0 Read Performance Excellent Read performance is excellent, scaling towards controller maximum speed as more disks are added. The use of multiple controllers will aid in scaling. Write Performance Excellent Write performance is excellent as well, typically scaling even better than reads. Space Efficiency Reliability ~100% Decreased Space efficiency is quite RAID-0 offers no good; there is very little protection against disk overhead. crashes; in fact, it is somewhat worse than non-RAID configurations because a single disk crash is guaranteed to affect the data spread out over the array. RAID-1: Mirroring RAID-1, or mirroring, means that the data is copied or mirrored across multiple physical disks. The data from a single physical disk or partition, once put into a RAID-1 array, will be copied transparently to the other disks in the array. This provides increased reliability for data integrity; should one disk fail, the data still remains on the other(s). Tip: Although RAID-1, as well as other RAID levels such as RAID-5, does provide some data protection, this is only protection against common hardware problems such as failure of a single disk. RAID should not be viewed as a substitute for regular data back-ups. Since it is possible to read from two (or more) disks at once, there is a possible performance increase using RAID-1. Typically performance is sacrificed for recovery of data. Because data is mirrored, only half of the physical space is utilized, and data must be replicated to multiple disks, marginally increasing write times. Software RAID-1 is supported by HP Linux workstations. Figure 2. Efficiency of Software RAID-1 Read Performance Write Performance Space Efficiency Slight Improvement Somewhat Slower ~50% Theoretically, RAID-1 configuration could deliver higher read performance, but there have not been significant gains seen using software RAID-1. Writes will be Only 50% space fractionally slower than efficiency for two-disk non-RAID configurations RAID-1, since the data since data must be is fully replicated on replicated to several each disk. disks. Reliability Excellent Reliability is very good; if one disk crashes, the other(s) still have a full copy of the data. 5