HP dx7208 RAM Allocation with Microsoft Windows XP and HP Commercial Desktops - Page 3
How does the limit work?, What is being done? - bios
 |
View all HP dx7208 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 3 highlights
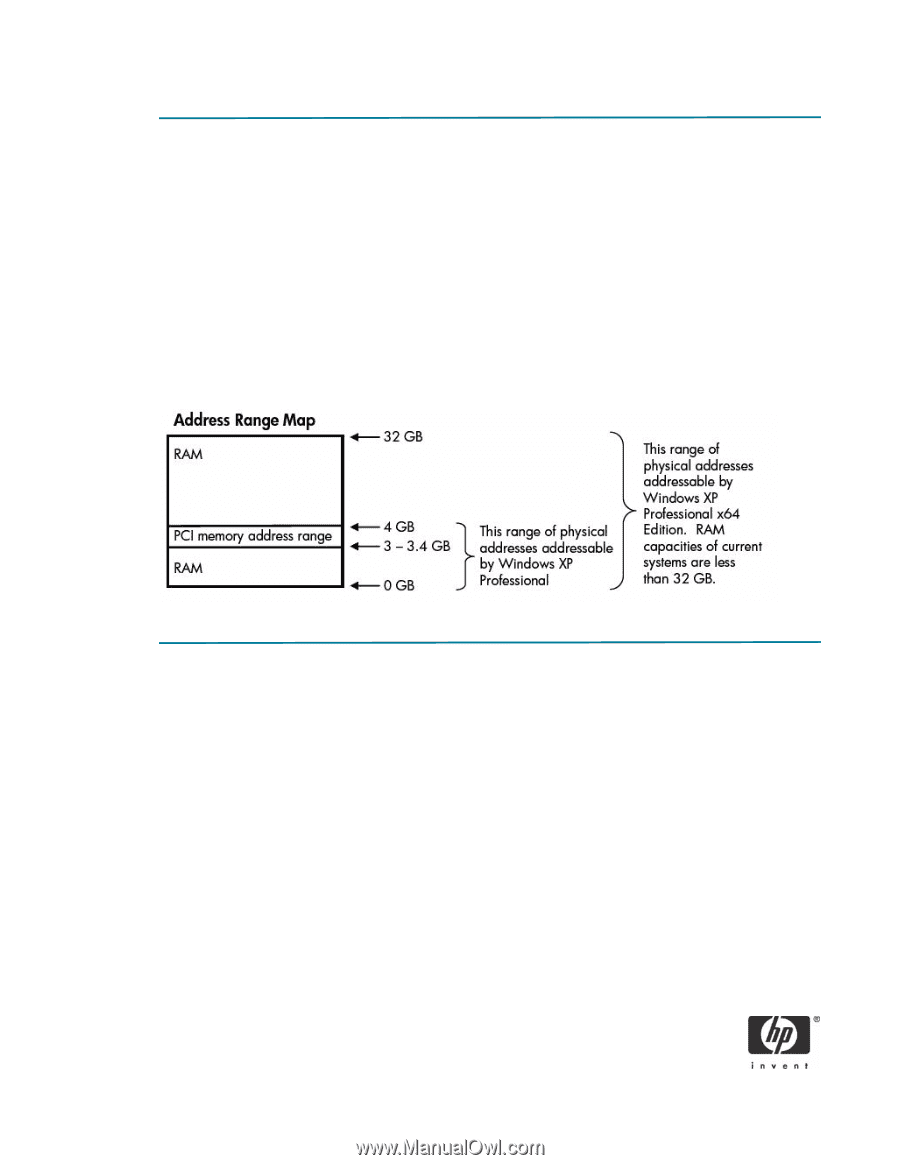
How does the limit work? Physical memory addresses are divided into two sections: the PCI memory address range (also known as Memory Mapped I/O), and the RAM available to the operating system. This explains why even with 4 GB of memory, available RAM is less than 4 GB. PCI memory address space is used to transfer data by the BIOS, I/O cards, networking, PCI hubs, bus bridges, PCI Express, and graphics cards. It starts at the top of memory at 4 GB and takes memory addressing to lower address ranges. PCI Express alone takes up 256 MB of address space, and each component also requires an additional amount. Therefore, it is very easy for a system with 4 GB of physical memory to lose 512 MB or more address space before any RAM addressing is allocated. RAM addressing starts at 0 MB and takes memory addresses to higher address ranges up to the bottom of the PCI memory address space, which is around 3 to 3.4 GB. The bottom of PCI memory address space may fall outside of this range depending on system configuration, especially if more than one graphics card is installed. What is being done? The 4 GB memory limitation is a well-known industry architectural problem, and HP is working toward a 64-bit commercial desktop solution. In the near future, HP commercial desktop PCs will have all the components (processor, chipset, and OS) necessary to support 64-bit computing with greater than 4 GB of physical memory. © 2006 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein. Microsoft, MS-DOS, Windows, and Windows NT are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the U.S. and other countries. 432234-001, 5/2006 3