Meade Polaris 90mm User Manual - Page 10
The Meade 4m Community
 |
View all Meade Polaris 90mm manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 10 highlights
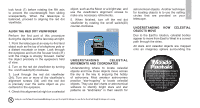
Earth. This mapping system is similar to the system of latitude and longitude on 8 Earth surface maps. In mapping the surface of the Earth, lines of longitude are drawn between the North and South Poles and lines of latitude are drawn in an East-West direction, parallel to the Earth's equator. Similarly, imaginary lines have been drawn to form a latitude Fig. 7 North Celestial Pole +90 Déc. (Vicinity of Star Polaris) Celestial Equator Declination 15 14 13 12 11 16 17 18 19 20 21 Rotation of the Earth 22 23 0 1 Right Ascension 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 0 Dec. South Celestial Pole -90 Dec. and longitude on the celestial sphere. These lines are known as Right Ascension and Declination. The celestial map also contains two poles and an equator just like a map of the Earth. The celestial poles are defined as those two points where the Earth's North and South poles, if extended to infinity, would cross the celestial sphere. Thus, the North Celestial Pole is that point in the sky where the North Pole crosses the celestial sphere. The North Star, Polaris, is located very near the North Celestial Pole. So, just as an object's position on the Earth's surface can be located by its latitude and longitude, celestial objects may also be located using Right Ascension and Declination. For example: You can locate Los Angeles, California, by its latitude (+34°) and longitude (118°). Similarly, you can locate the Ring Nebula (also known as "M57") by its Right Ascension (18hr) and its Declination (+33°). • RIGHT ASCENSION (R.A.): This Celestial version of longitude is measured in units of hours (hr), minutes (min), and seconds (sec) Looking at or near the Sun will cause irreversable damage to your eye. Do not point this telescope at or near the Sun. Do not look through the telescope as it is moving. on a 24 hour "clock" (similar to how Earth's time zones are determined by longitude lines). The "zero" line was chosen to pass through the constellation Pegasus, a sort of cosmic Greenwich meridian. R.A. coordinates range from 0hr 0min 0sec to 23hr 59min 59sec. There are 24 primary lines of R.A., located at 15-degree intervals along the celestial equator. Objects located further and further East of the zero R.A. grid line (0hr 0min 0sec) carry higher R.A. coordinates. • Declination (Dec.): This celestial version of latitude is measured in degrees, arcminutes, and arc-seconds (e.g., 15° 27' 33"). Dec. locations North of the celestial equator are indicated with a plus (+) sign (e.g., the Dec. of the North celestial pole is +90°). Any point on the celestial equator (such as the THE MEADE 4M COMMUNITY You haven't just bought a telescope, you have embarked on an astronomy adventure that never ends. Share the journey with others by accepting your free membership in the 4M community of astronomers. Go to www.Meade4M.com to activate your membership today.