Netgear MBR1310 MBR1310 User Manual - Page 91
Troubleshoot the ISP Connection, Connect to the Internet, Troubleshoot Internet Browsing
 |
View all Netgear MBR1310 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 91 highlights
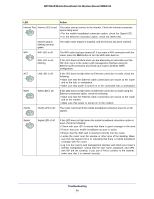
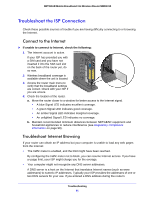
NETGEAR Mobile Broadband 11n Wireless Router MBR1310 Troubleshoot the ISP Connection Check these possible sources of trouble if you are having difficulty connecting to or browsing the Internet. Connect to the Internet If unable to connect to Internet, check the following: 1. The Internet account is active. If your ISP has provided you with a SIM card and you have not inserted it into the SIM card slot on the back of the router yet, do so now. 2. Wireless broadband coverage is available where the unit is located. 3. Access the router main menu to verify that the broadband settings are correct. Check with your ISP if you are unsure. 4. Check the location of the router. a. Move the router closer to a window for better access to the Internet signal. • A blue Signal LED indicates excellent coverage. • A green Signal LED indicates good coverage. • An amber Signal LED indicates marginal coverage. • An unlighted Signal LED indicates no coverage. b. Maintain recommended minimum distances between NETGEAR equipment and household appliances to reduce interference (see Regulatory Compliance Information on page 98). Troubleshoot Internet Browsing If your router can obtain an IP address but your computer is unable to load any web pages from the Internet: • The traffic meter is enabled, and the limit might have been reached. By configuring the traffic meter not to block, you can resume Internet access. If you have a usage limit, your ISP might charge you for the overage. • Your computer might not recognize any DNS server addresses. A DNS server is a host on the Internet that translates Internet names (such as www addresses) to numeric IP addresses. Typically your ISP provides the addresses of one or two DNS servers for your use. If you entered a DNS address during the router's Troubleshooting 91