Netgear WGR614 WGR614v6 Reference Manual - Page 53
Advanced Configuration of the Router, Configuring Port Triggering - port forwarding
 |
UPC - 606449027600
View all Netgear WGR614 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 53 highlights
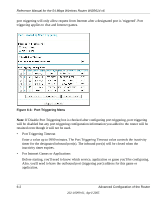
Chapter 6 Advanced Configuration of the Router This chapter describes how to configure the advanced features of your 54 Mbps Wireless Router WGR614 v6. These features can be found under the Advanced heading in the Main Menu of the browser interface. . Note: If you are unfamiliar with networking and routing, refer to Appendix B, "Network, Routing, Firewall, and Basics," to become more familiar with the terms and procedures used in this chapter. Configuring Port Triggering Port Triggering is an advanced feature that can be used to easily enable gaming and other internet applications. Port Forwarding is typically used to enable similar functionality, but it is static and has some limitations. Note: If you use applications such as multi-player gaming, peer-to-peer connections, real time communications such as instant messaging, or remote assistance (a feature in Windows XP), you should also enable UPnP according to the instructions at "Using Universal Plug and Play (UPnP)" on page 6-18. Port Triggering opens an incoming port temporarily and does not require the server on the internet to track your IP address if it is changed by DHCP, for example. Port Triggering monitors outbound traffic. When the router detects traffic on the specified outbound port, it remembers the IP address of the computer that sent the data and triggers the incoming port. Incoming traffic on the triggered port is then forwarded to the triggering computer. Using the Port Triggering page, you can make local computers or servers available to the Internet for different services (for example, FTP or HTTP), to play Internet games (like Quake III), or to use Internet applications (like CUseeMe). Port Forwarding is designed for FTP, Web Server or other server based services. Once port forwarding is set up, request from Internet will be forwarded to the proper server. On the contrary, Advanced Configuration of the Router 6-1 202-10099-01, April 2005